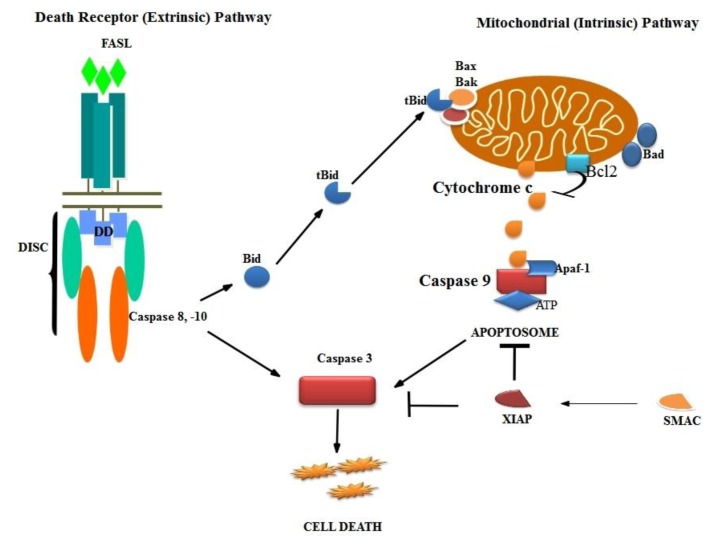
Figure 3.
Pathway of apoptosis. Extrinsic cell death pathway is mediated by a TNF receptor superfamily, called the death receptors. Receptor-mediated cell death is initiated by the recruitment of adapter proteins, like FADD (Fas associated death domain), via the DD (death domain), which then bind to the death effector domain-containing caspase-8 or -10. Formation of this DISC (death inducing signaling complex) results in the activation of caspase-8/10, which then directly cleaves and activates the executioner caspase-3. Mitochondrial or intrinsic pathway, proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members, Bax and Bak, translocate to the mitochondria. The BH3-only protein Bid activates Bax and Bak oligomerisation form an oligomeric pore in the outer mitochondrial membrane. This results in the release of cytochrome c and other pro-apoptotic factors from the mitochondria to the cytosol. Cytochrome c triggers the assembly of the apoptosome (Apaf-1, caspase-9 and also the nucleotide adenosine tri phosphate (ATP) as a third component, binds and forms apoptosome). Subsequently, apoptosome activates caspase-3 and cell death. IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis protein) binds directly to caspases and inhibits their enzymatic activity. The inhibitory function of IAPs is controlled by the SMAC (Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases).