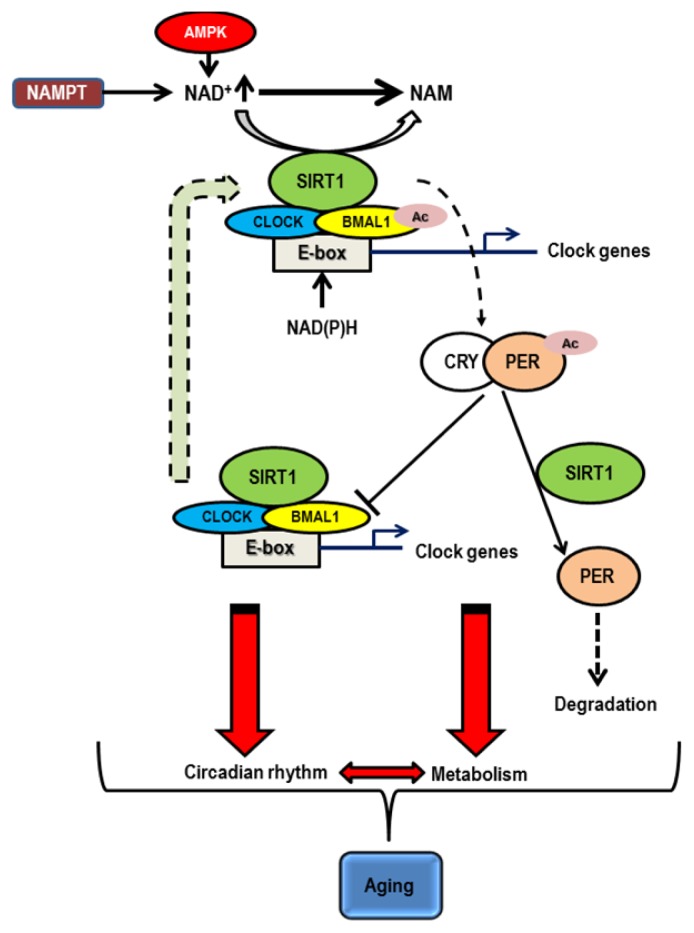
Figure 2.
A representation of SIRT1- mediated regulation of the circadian clock and metabolism impacting aging. SIRT1 interacts with CLOCK, which heterodimerizes with BMAL1. BMAL1 is deacetylated by SIRT1 in a circadian manner and promotes expression of clock genes. Additionally, SIRT1 interacts with and deacetylates PER2 (in mammals) which heterodimerizes with CRY proteins to inhibit CLOCK-BMAL1 function and promotes its degradation. NAD+ from AMPK and NAMPT is a key regulator for SIRT1 function. Synchronous expression of clock genes results in regulation of clock controlled genes (CCGs) which impact metabolism and hence aging.