Abstract
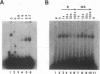
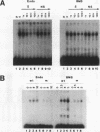
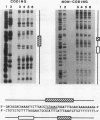
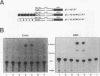
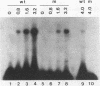
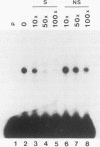
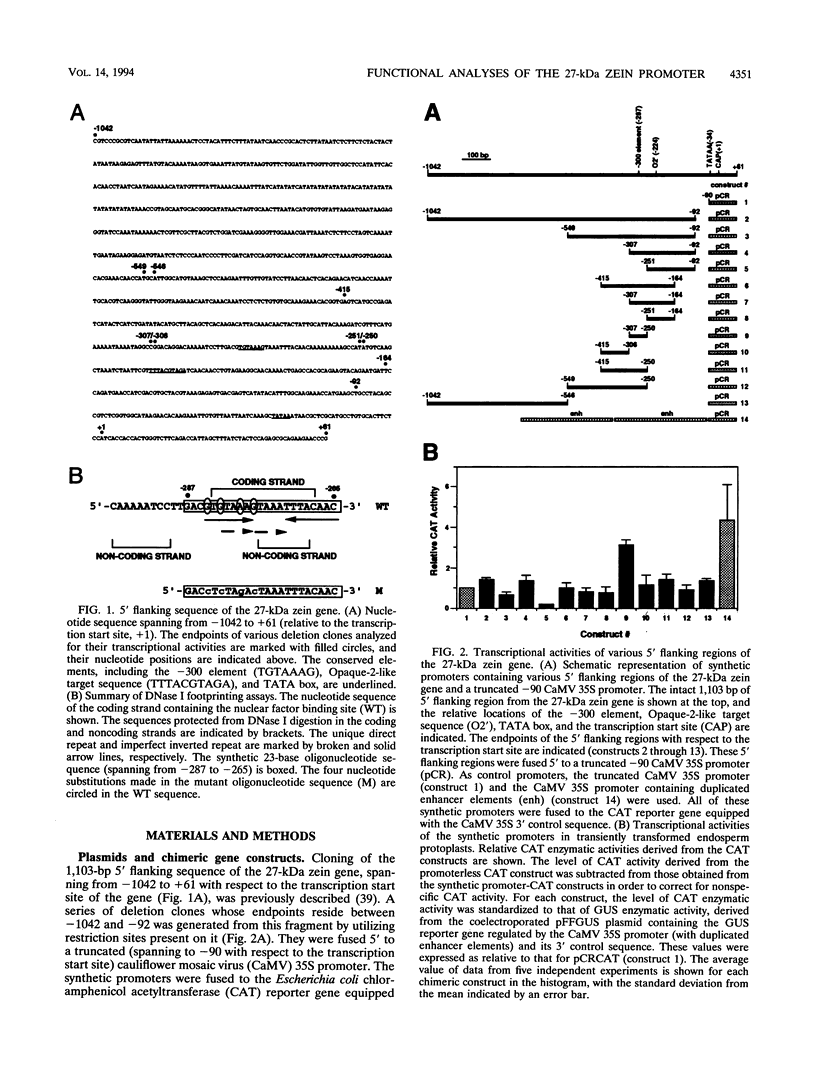
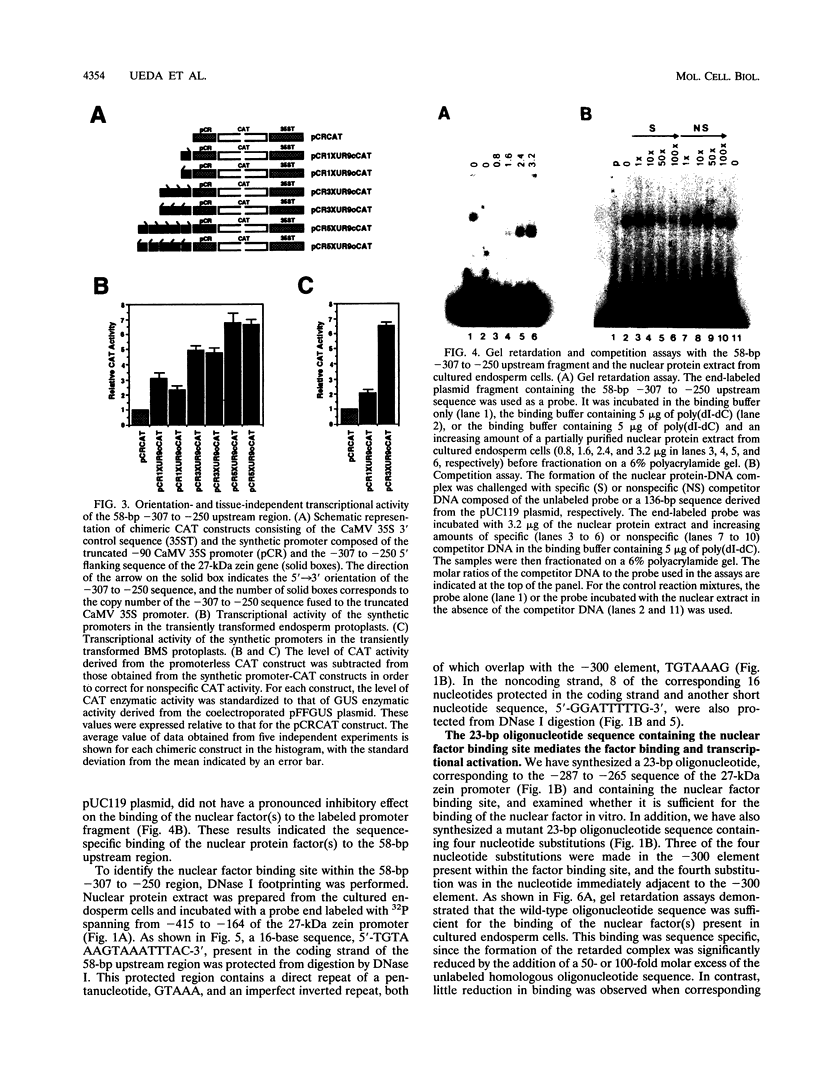
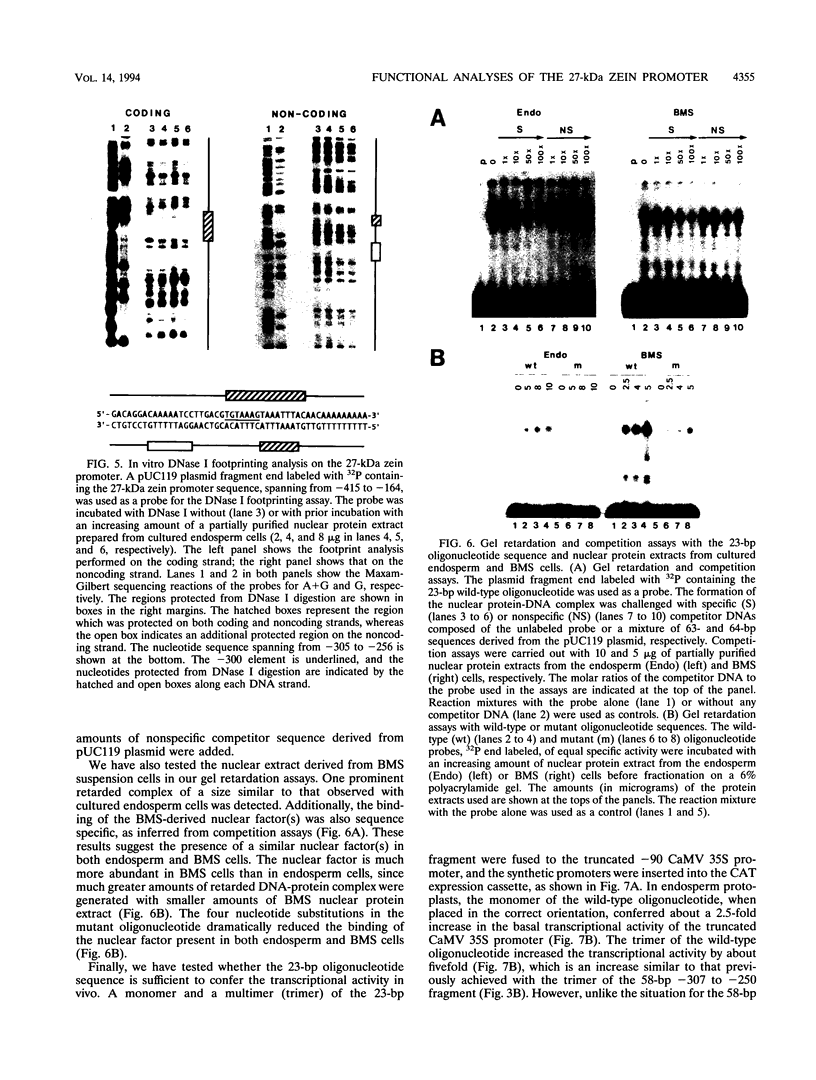
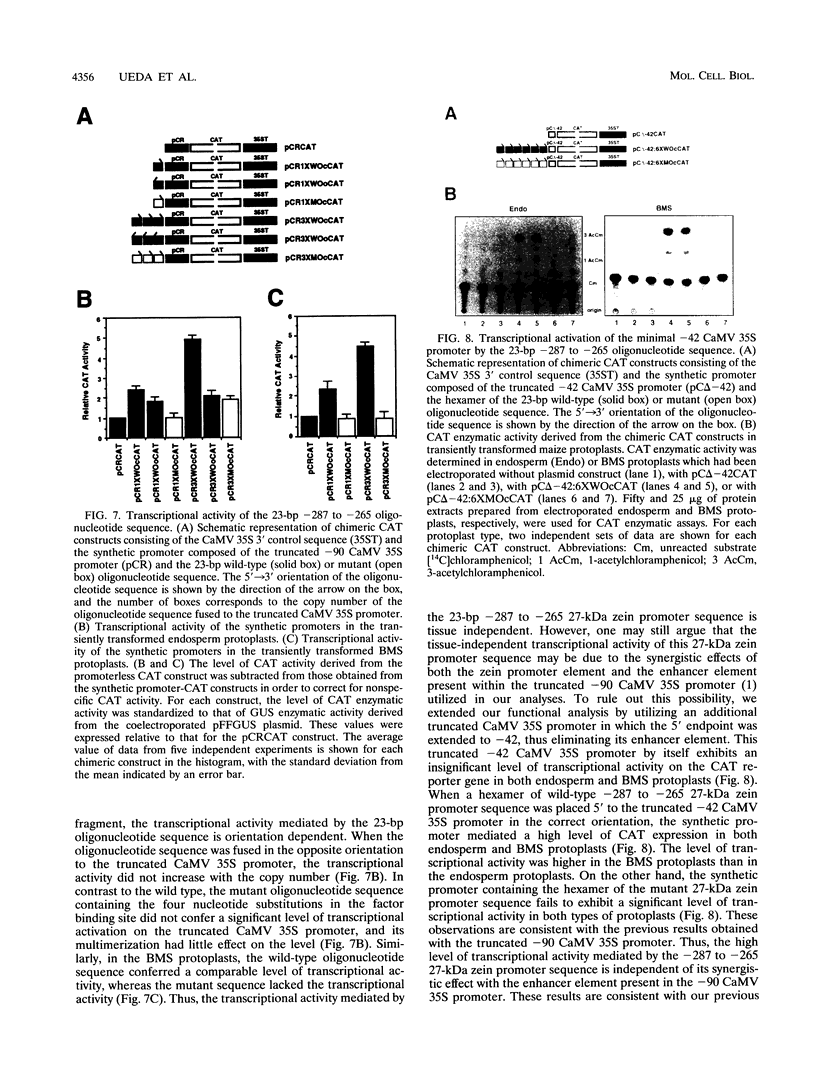
By utilizing a homologous transient-expression system, we have shown that a 58-bp sequence from the gamma-class 27-kDa zein promoter, spanning from -307 to -250 relative to the transcription start site, confers a high level of transcriptional activity on a truncated plant viral promoter. The transcriptional activity mediated by the 58-bp sequence is orientation independent, and it is further enhanced as a result of its multimerization. A similarly high level of transcriptional activity was also observed in protoplasts isolated from leaf tissue-derived maize suspension cells. In vitro binding and DNase I footprinting assays with nuclear protein prepared from cultured endosperm cells revealed the sequence-specific binding of a nuclear factor(s) to a 16-nucleotide sequence present in the 58-bp region. The nuclear factor binding sequence includes the -300 element, a cis-acting element highly conserved among different zein genes and many other cereal storage protein genes. A 23-bp oligonucleotide sequence containing the nuclear factor binding site is sufficient for binding the nuclear factor in vitro. It also confers a high level of transcriptional activity in vivo, but in an orientation-dependent manner. Four nucleotide substitutions in the -300 element drastically reduced binding and transcriptional activation by the nuclear factor. The same nuclear factor is abundant in the developing kernel endosperm and binds to the -300 element region of the 27-kDa or the alpha-class zein promoter. These results suggest that the highly conserved -300 element is involved in the common regulatory mechanisms mediating the coordinated expression of the zein genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. Tissue-specific expression from CaMV 35S enhancer subdomains in early stages of plant development. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1677–1684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A., St John T. P., Thomas M., Davis R. W. Zein storage protein gene family of maize. An assessment of heterogeneity with cloned messenger RNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colot V., Robert L. S., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W., Thompson R. D. Localization of sequences in wheat endosperm protein genes which confer tissue-specific expression in tobacco. EMBO J. 1987;6(12):3559–3564. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Alvarez M., Kirihara J. A., Messing J. Post-transcriptional regulation of methionine content in maize kernels. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Feb;225(2):331–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00269866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das O. P., Messing J. W. Allelic variation and differential expression at the 27-kilodalton zein locus in maize. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4490–4497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das O. P., Poliak E., Ward K., Messing J. A new allele of the duplicated 27kD zein locus of maize generated by homologous recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3325–3330. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esen A. Separation of alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) from maize into three fractions by differential solubility. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):623–627. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geetha K. B., Lending C. R., Lopes M. A., Wallace J. C., Larkins B. A. opaque-2 modifiers increase gamma-zein synthesis and alter its spatial distribution in maize endosperm. Plant Cell. 1991 Nov;3(11):1207–1219. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.11.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen G., Rubenstein I. Complex organization of zein genes in maize. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond-Kosack M. C., Holdsworth M. J., Bevan M. W. In vivo footprinting of a low molecular weight glutenin gene (LMWG-1D1) in wheat endosperm. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):545–554. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirihara J. A., Petri J. B., Messing J. Isolation and sequence of a gene encoding a methionine-rich 10-kDa zein protein from maize. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodrzycki R., Boston R. S., Larkins B. A. The opaque-2 mutation of maize differentially reduces zein gene transcription. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):105–114. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz A. L., Boston R. S., Larkins B. A. Structural and transcriptional analysis of DNA sequences flanking genes that encode 19 kilodalton zeins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):90–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00331495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier U. G., Brown J. W., Tologcyzki C., Feix G. Binding of a nuclear factor to a consensus sequence in the 5' flanking region of zein genes from maize. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):17–22. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier U. G., Grasser K. D., Haass M. M., Feix G. Multiple proteins bind to the P2 promoter region of the zein gene pMS1 of maize. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):164–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00261716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. D., Lindell J. S., Larkins B. A. Quantitative analysis of the accumulation of Zein mRNA during maize endosperm development. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16445–16450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzke A. J., Stöger E. M., Schernthaner J. P., Matzke M. A. Deletion analysis of a zein gene promoter in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Mar;14(3):323–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00028769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. K., Bauer W. D. Rhizobium attachment to clover roots. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;2:333–345. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_2.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Knudsen S. The nitrogen response of a barley C-hordein promoter is controlled by positive and negative regulation of the GCN4 and endosperm box. Plant J. 1993 Aug;4(2):343–355. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04020343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Argos P., Naravana S. V., Larkins B. A. Sequence analysis and characterization of a maize gene encoding a high-sulfur zein protein of Mr 15,000. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6279–6284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Devereux J., Wilson D. R., Sheldon E., Larkins B. A. Cloning and sequence analysis reveal structural variation among related zein genes in maize. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle T., Feix G. Functional analysis of the -300 region of maize zein genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Feb;231(3):369–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00292705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. J., Ketudat M., Aukerman M. J., Hoschek G. Opaque-2 is a transcriptional activator that recognizes a specific target site in 22-kD zein genes. Plant Cell. 1992 Jun;4(6):689–700. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.6.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotwell M. A., Boyer S. K., Chesnut R. S., Larkins B. A. Analysis of seed storage protein genes of oats. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9652–9658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So J. S., Larkins B. A. Binding of an endosperm-specific nuclear protein to a maize beta-zein gene correlates with zein transcriptional activity. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Sep;17(3):309–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00040627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Boston R. S., Lyznik L. A., Hodges T. K., Larkins B. A. Analysis of promoter activity from an alpha-zein gene 5' flanking sequence in transient expression assays. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Nov;15(5):755–764. doi: 10.1007/BF00016125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Larkins B. A. Structural elements regulating zein gene expression. Bioessays. 1989 Apr;10(4):108–113. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans M. C., Maliga P., Vieira J., Messing J. The pFF plasmids: cassettes utilising CaMV sequences for expression of foreign genes in plants. J Biotechnol. 1990 Jun;14(3-4):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(90)90117-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Messing J. Manipulation of amino acid balance in maize seeds. Genet Eng (N Y) 1993;15:109–130. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1666-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Waverczak W., Ward K., Sher N., Ketudat M., Schmidt R. J., Messing J. Mutations of the 22- and 27-kD zein promoters affect transactivation by the Opaque-2 protein. Plant Cell. 1992 Jun;4(6):701–709. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werr W., Frommer W. B., Maas C., Starlinger P. Structure of the sucrose synthase gene on chromosome 9 of Zea mays L. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1373–1380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Larkins B. A. Zein gene organization in maize and related grasses. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(3-4):330–340. doi: 10.1007/BF02104739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]