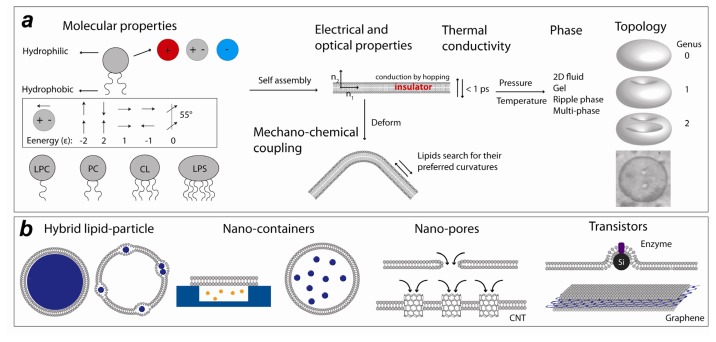
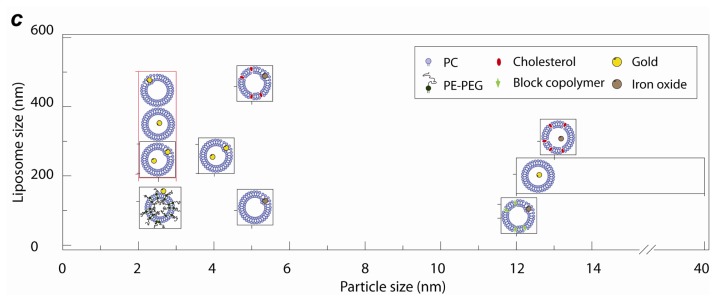
Figure 1.
(a) Physico-chemical properties of phospholipids. Phospholipids are composed of a hydrophilic head group and hydrophobic tails (N = 1–6). PC: phosphatidylcholine, LPC: LysoPC, CL: cardiolipin, LPS: lipopolysaccharide. The head group may carry a positive or negative charge. It may also be neutral but possess a significant electric dipole which enforces particular arrangements in the monolayer and bilayer assemblies. Self assembly of phospholipids results in bilayers or monolayers. Bilayers are birefringent [28], thermally conductive (energy transfer on sub-picosecond time scales; κ~several Watt/mK [20]), behave as insulators perpendicular to the membrane and in the core part whereas they are electrically conductive within the plane of the membrane due to proton hopping in the interfacial water [29]. Assembled bilayers display different phases depending on the temperature (T) and pressure (P) of the environment. The fluid bilayer is also deformable and introducing curvature may lead to spatial redistribution of lipids, some preferring certain curved regions. Lipid bilayer can form topologically rich structures: a spherical bilayer (genus 0) vesicle, a genus 1 and a genus 2 vesicle [17,19] are shown. In addition to phospholipids, also other lipids such as sterols have been used in nanotechnological applications; (b) Lipid based nano-devices. Two examples of hybrid lipid particles are presented: in one case the particles are enclosed by the vesicle and in the other case the particles are embedded in between the leaflets. Nano-containers can be formed when a hard nano well is sealed by a lipid bilayer. Membrane pores can be generated within a bilayer by applying voltages or with the help of carbon nanotubes functionalized with hydrophilic groups at their ends. A composite structure made of silicon nano-wire and enzyme functionalized lipid bilayer is shown. Another example of lipid based nanostructures with applications in electronics is lipid bilayer-graphene hybrid where graphene is embedded in between the leaflets of a bilayer and thereby the graphene’s physical properties are modulated; (c) Liposomes functionalized with nanoparticles allowing for radiation/magnetic field triggered cargo release [30–36]. The ticks on the box sides indicate the size or the size range of the synthesized particles.