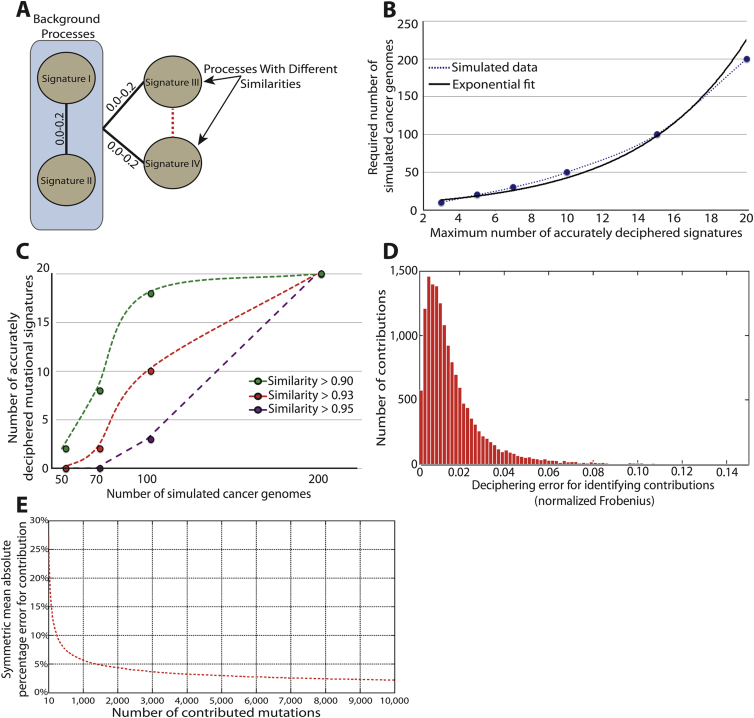
Figure S1.
Additional Factors Affecting the Efficacy of Deciphering Mutational Signatures with Simulated Data, Related to Figure 3
(A) Design for simulating the signatures of four mutational processes with different similarities between them. Signatures I and II differ significantly from each other as well as from the other two Signatures (cosine similarity between 0.00 and 0.20). Signatures III and IV were simulated with varying similarities between them.
(B) Dependency between accurately deciphered signatures (i.e., cosine similarity between simulated and deciphered signature > 0.95) and the number of mutational catalogs needed to decipherer these signatures.
(C) Identifying the maximum number of accurately deciphered signatures (cosine similarity between simulated and deciphered signature shown in the legend) from sets of mutational catalogs simulated using the signatures of 20 mutational processes.
(D) Distribution of the normalized Frobenius error for identifying the contributions of accurately deciphered signatures of mutational processes (i.e., cosine similarity between simulated and deciphered signature > 0.95).
(E) Average symmetric mean absolute percentage error for identifying the contributions of accurately deciphered signatures of mutational processes (i.e., cosine similarity between simulated and deciphered signature > 0.95) based on the number mutations contributed by the signature.