Abstract
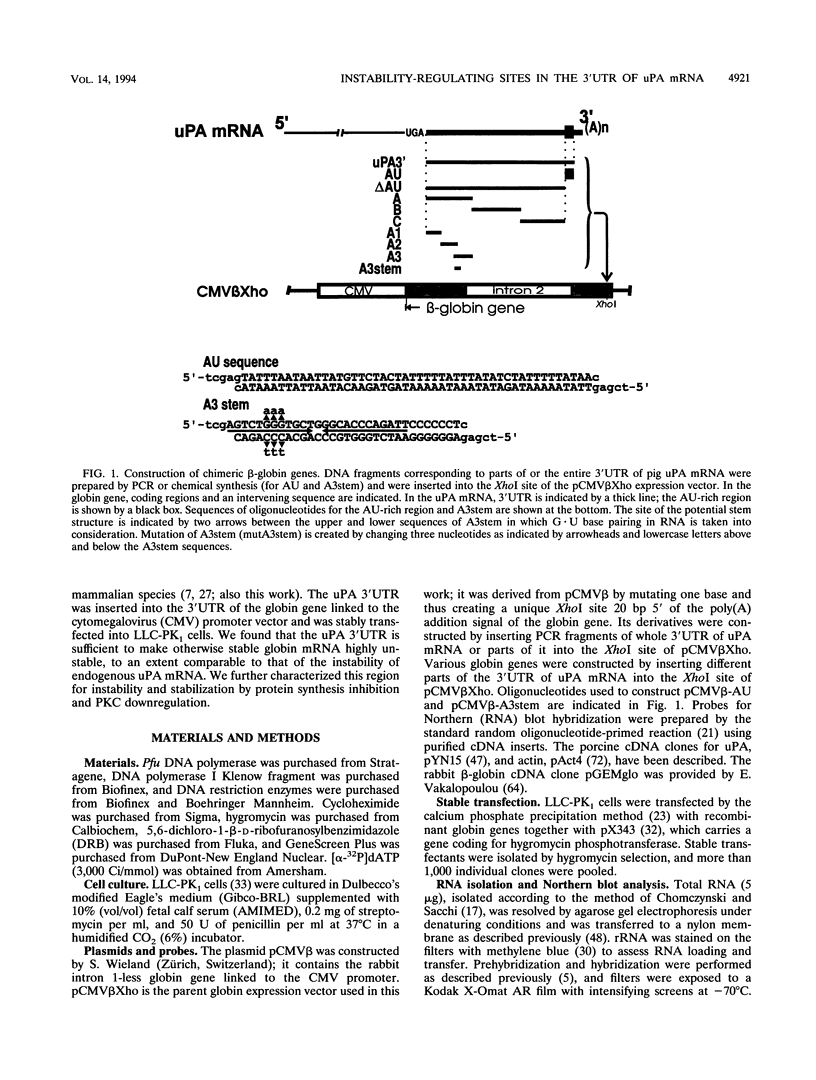
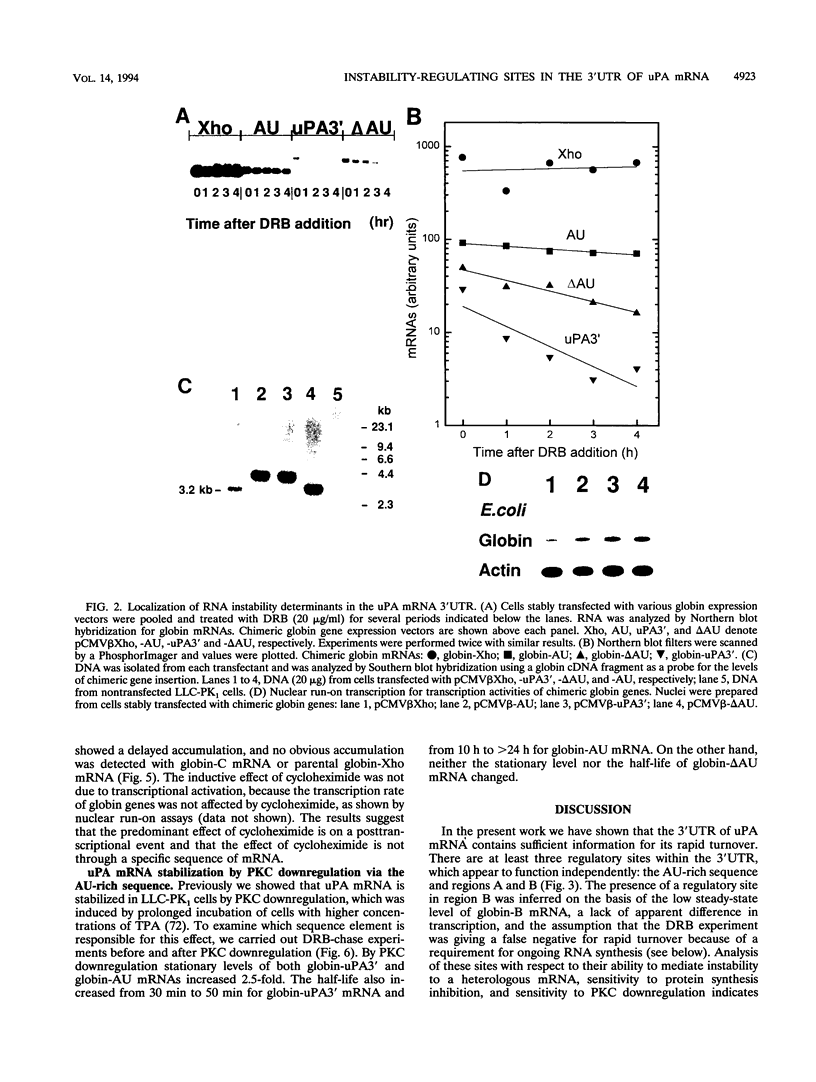
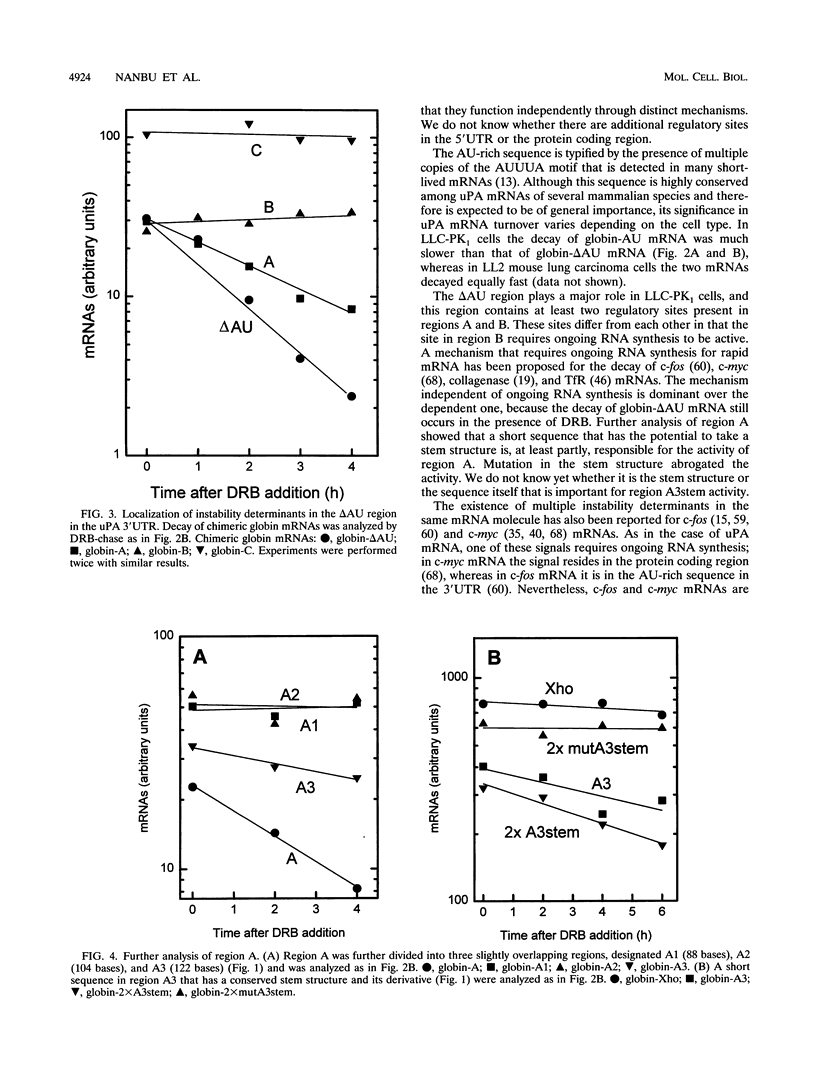
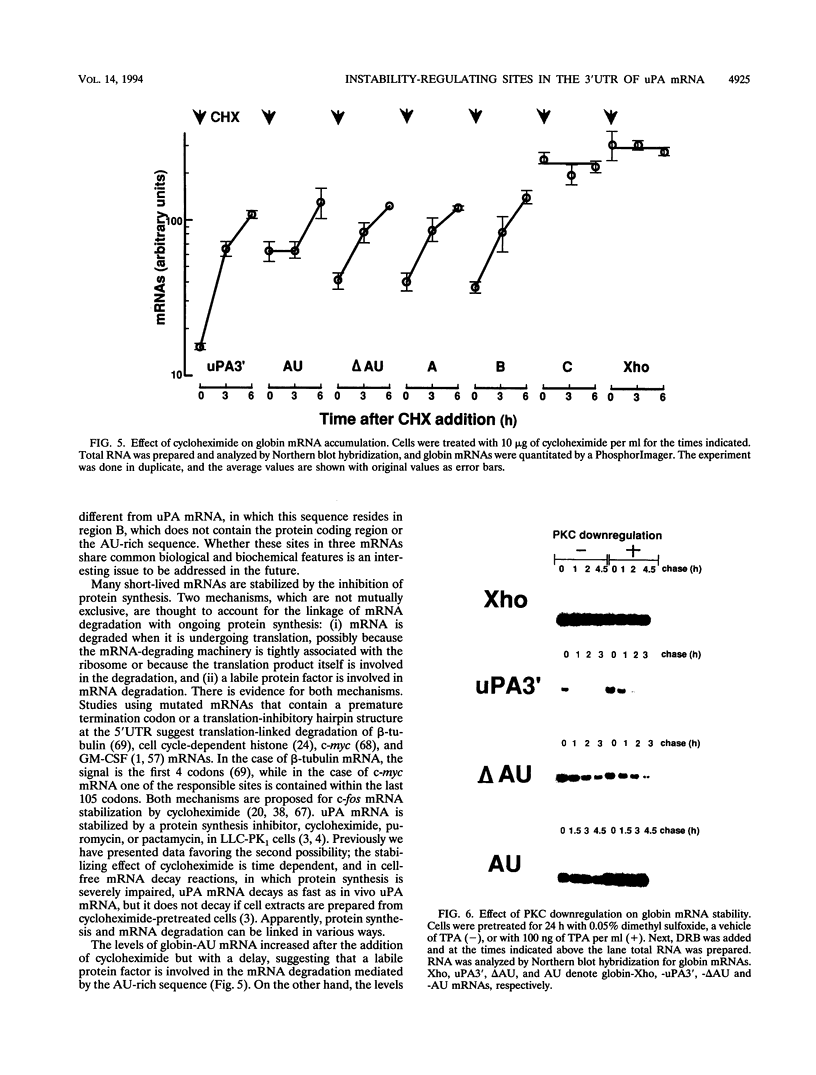
In LLC-PK1 cells urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) mRNA has a short half-life. It is stabilized by inhibition of protein synthesis and by downregulation of protein kinase C (PKC). In the present study on uPA mRNA metabolism, we focused our attention on the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of the uPA mRNA, as this region is long and highly conserved among several mammalian species, including mice and humans. To investigate the possible role of the 3'UTR of uPA mRNA in mRNA metabolism, we inserted this region into the 3'UTR of the rabbit beta-globin gene that is linked to the cytomegalovirus promoter and stably transfected it into LLC-PK1 cells. While the parental globin mRNA was stable, the chimeric mRNA was degraded as rapidly as endogenous uPA mRNA, suggesting that the 3'UTR of uPA mRNA contains most of the information required for its rapid turnover. Further analysis showed that there are at least three independent determinants of instability in the 3'UTR; one is an AU-rich sequence located immediately 3' of the poly(A) addition signal, and one is a sequence containing a stem structure. One determinant seems to require ongoing RNA synthesis for its activity. All chimeric unstable globin mRNAs became stable in the presence of cycloheximide, a protein synthesis inhibitor, suggesting that the stabilization of mRNA by protein synthesis inhibition is not through a specific sequence in the mRNA. In PKC-downregulated cells, globin mRNAs with the complete 3'UTR or the AU-rich sequence were stabilized, suggesting that PKC downregulation stabilizes uPA mRNA through the AU-rich sequence. Here we discuss the significance of multiple, independently acting instability determinants in the regulation of uPA mRNA metabolism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharon T., Schneider R. J. Selective destabilization of short-lived mRNAs with the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor AU-rich 3' noncoding region is mediated by a cotranslational mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1971–1980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akashi M., Shaw G., Gross M., Saito M., Koeffler H. P. Role of AUUU sequences in stabilization of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor RNA in stimulated cells. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):2005–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altus M. S., Nagamine Y. Protein synthesis inhibition stabilizes urokinase-type plasminogen activator mRNA. Studies in vivo and in cell-free decay reactions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21190–21196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altus M. S., Pearson D., Horiuchi A., Nagamine Y. Inhibition of protein synthesis in LLC-PK1 cells increases calcitonin-induced plasminogen-activator gene transcription and mRNA stability. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):387–392. doi: 10.1042/bj2420387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrus L., Altus M. S., Pearson D., Grattan M., Nagamine Y. hsp70 mRNA accumulates in LLC-PK1 pig kidney cells treated with calcitonin but not with 8-bromo-cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6183–6187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aström J., Aström A., Virtanen A. In vitro deadenylation of mammalian mRNA by a HeLa cell 3' exonuclease. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3067–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Vassalli J. D., Combépine C., Godeau F., Nagamine Y., Reich E., Kocher H. P., Duvoisin R. M. Cloning, nucleotide sequencing and expression of cDNAs encoding mouse urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P. L., Herrick D. J., Prokipcak R. D., Ross J. Control of c-myc mRNA half-life in vitro by a protein capable of binding to a coding region stability determinant. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):642–654. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T. An inducible cytoplasmic factor (AU-B) binds selectively to AUUUA multimers in the 3' untranslated region of lymphokine mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3288–3295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. An A + U-rich element RNA-binding factor regulates c-myc mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2460–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Plucinska I. M., Sheldon L. A., O'Connor G. T. Half-life of synovial cell collagenase mRNA is modulated by phorbol myristate acetate but not by all-trans-retinoic acid or dexamethasone. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6378–6384. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Koeller D. M., Ramin V. C., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA levels requires iron-responsive elements and a rapid turnover determinant in the 3' untranslated region of the mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3693–3699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., You Y., Shyu A. B. Two cellular proteins bind specifically to a purine-rich sequence necessary for the destabilization function of a c-fos protein-coding region determinant of mRNA instability. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5748–5757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. Y., Amara F. M., Wright J. A. Mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 mRNA stability under normal and phorbol ester stimulating conditions: involvement of a cis-trans interaction at the 3' untranslated region. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3977–3986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen J. L., Estensen R. D., Nagamine Y., Reich E. Induction and desensitization of plasminogen activator gene expression by tumor promoters. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12426–12433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delany A. M., Brinckerhoff C. E. Post-transcriptional regulation of collagenase and stromelysin gene expression by epidermal growth factor and dexamethasone in cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Dec;50(4):400–410. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Mahadevan L. C. Protein synthesis inhibitors differentially superinduce c-fos and c-jun by three distinct mechanisms: lack of evidence for labile repressors. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorospe M., Kumar S., Baglioni C. Tumor necrosis factor increases stability of interleukin-1 mRNA by activating protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6214–6220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton B. J., Nagy E., Malter J. S., Arrick B. A., Rigby W. F. Association of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 and C proteins with reiterated AUUUA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8881–8887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. R., Kefford R. F. Conservation and potential role of RNA-instability motifs in urokinase gene 3'-untranslated sequences. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Aug 7;83(15):1103–1104. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.15.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. R., McDonald D. A., Kefford R. F. Post-transcriptional regulation of urokinase plasminogen activator gene expression occurs in the nucleus of BC1 rat mammary tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 1992 Apr 1;50(6):918–923. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. R., Tansey W. P., Phillips S. M., Ramshaw I. A., Kefford R. F. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional activation of urokinase plasminogen activator gene expression in metastatic tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1992 May 1;52(9):2489–2496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin D. L., Schmidt G. W. Rapid, reversible staining of northern blots prior to hybridization. Biotechniques. 1988 Mar;6(3):196-7, 199-200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter P., Kikinis Z., Altus M. S., Pearson D., Nagamine Y. A new genetic approach for studying hormonal regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in LLC-PK1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4535–4541. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. N., Cherry W. R., Weaver G. W. The origin and characteristics of a pig kidney cell strain, LLC-PK. In Vitro. 1976 Oct;12(10):670–677. doi: 10.1007/BF02797469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai Y., Akahane K., Pluznik D. H., Cohen R. B. Ca2+ ionophore A23187-dependent stabilization of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor messenger RNA in murine thymoma EL-4 cells is mediated through two distinct regions in the 3'-untranslated region. J Immunol. 1993 May 15;150(10):4386–4394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Cole M. D. Rapid cytoplasmic turnover of c-myc mRNA: requirement of the 3' untranslated sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4513–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptain S., Downey W. E., Tang C., Philpott C., Haile D., Orloff D. G., Harford J. B., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D. A regulated RNA binding protein also possesses aconitase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10109–10113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Rouault T. A., Harford J. B. Regulating the fate of mRNA: the control of cellular iron metabolism. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90046-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeller D. M., Horowitz J. A., Casey J. L., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Translation and the stability of mRNAs encoding the transferrin receptor and c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7778–7782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krätzschmar J., Haendler B., Kojima S., Rifkin D. B., Schleuning W. D. Bovine urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor: cloning and induction by retinoic acid. Gene. 1993 Mar 30;125(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90325-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird-Offringa I. A. What determines the instability of c-myc proto-oncogene mRNA? Bioessays. 1992 Feb;14(2):119–124. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. J., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F., Skoultchi A. I. Coupling of replication type histone mRNA levels to DNA synthesis requires the stem-loop sequence at the 3' end of the mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6189–6193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine T. D., Gao F., King P. H., Andrews L. G., Keene J. D. Hel-N1: an autoimmune RNA-binding protein with specificity for 3' uridylate-rich untranslated regions of growth factor mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3494–3504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S., Hong Y. A redox switch and phosphorylation are involved in the post-translational up-regulation of the adenosine-uridine binding factor by phorbol ester and ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3167–3171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S. Identification of an AUUUA-specific messenger RNA binding protein. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2814487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F. Histone 3' ends: essential and regulatory functions. Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):93–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Pearson D., Altus M. S., Reich E. cDNA and gene nucleotide sequence of porcine plasminogen activator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9525–9541. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Sudol M., Reich E. Hormonal regulation of plasminogen activator mRNA production in porcine kidney cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1181–1190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanbu R., Kubo T., Hashimoto T., Natori S. Purification of an AU-rich RNA binding protein from Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) and its identification as a Thiolase. J Biochem. 1993 Sep;114(3):432–437. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Jacobson A. Translation and a 42-nucleotide segment within the coding region of the mRNA encoded by the MAT alpha 1 gene are involved in promoting rapid mRNA decay in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2780–2784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei R., Calame K. Differential stability of c-myc mRNAS in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2860–2868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Brewer G., Bernstein P., Hart P. A., Ross J. Regulation of mRNA turnover in eukaryotic cells. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(2):99–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone-Bizzozero N. I., Cansino V. V., Kohn D. T. Posttranscriptional regulation of GAP-43 gene expression in PC12 cells through protein kinase C-dependent stabilization of the mRNA. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1263–1270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccio A., Grimaldi G., Verde P., Sebastio G., Boast S., Blasi F. The human urokinase-plasminogen activator gene and its promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2759–2771. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Deardorff J. A. Translation initiation requires the PAB-dependent poly(A) ribonuclease in yeast. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):961–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B. Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80043-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savant-Bhonsale S., Cleveland D. W. Evidence for instability of mRNAs containing AUUUA motifs mediated through translation-dependent assembly of a > 20S degradation complex. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1927–1939. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Belasco J. G., Greenberg M. E. Two distinct destabilizing elements in the c-fos message trigger deadenylation as a first step in rapid mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):221–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. M., Carter B. Z., Pekala P. H., Malter J. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced glucose transporter (GLUT-1) mRNA stabilization in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Regulation by the adenosine-uridine binding factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8336–8341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunitha I., Slobin L. I. An in vitro system derived from Friend erythroleukemia cells to study messenger RNA stability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):560–568. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm I., Sehgal P. B. Halobenzimidazole ribosides and RNA synthesis of cells and viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1978;22:187–258. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakalopoulou E., Schaack J., Shenk T. A 32-kilodalton protein binds to AU-rich domains in the 3' untranslated regions of rapidly degraded mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3355–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wager R. E., Assoian R. K. A phorbol ester-regulated ribonuclease system controlling transforming growth factor beta 1 gene expression in hematopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5983–5990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisdom R., Lee W. The protein-coding region of c-myc mRNA contains a sequence that specifies rapid mRNA turnover and induction by protein synthesis inhibitors. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):232–243. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You Y., Chen C. Y., Shyu A. B. U-rich sequence-binding proteins (URBPs) interacting with a 20-nucleotide U-rich sequence in the 3' untranslated region of c-fos mRNA may be involved in the first step of c-fos mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2931–2940. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A., Hagmann J., Kiefer B., Nagamine Y. Ca2+ potentiates cAMP-dependent expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene through a calmodulin- and protein kinase C-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21194–21201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A., Knesel J., Fabbro D., Nagamine Y. Protein kinase C down-regulation enhances cAMP-mediated induction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator mRNA in LLC-PK1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21067–21074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]