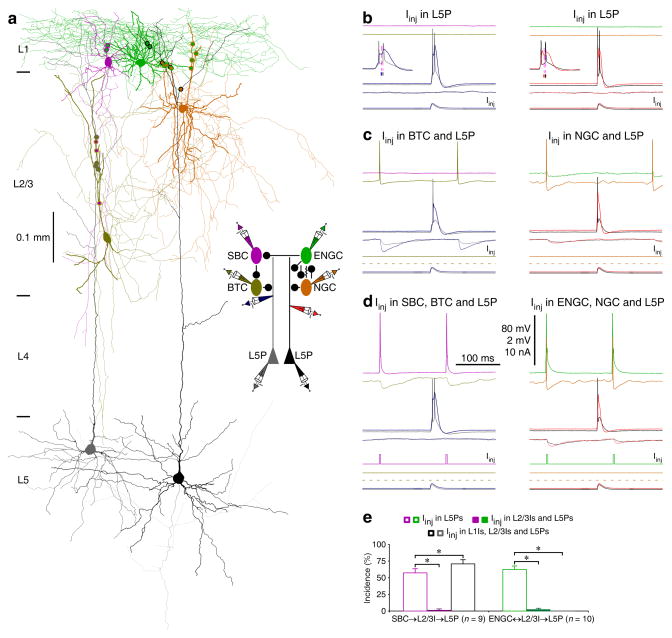
Fig. 7. SBC→ and ENGC↔L2/3I→L5 pyramidal neuronal circuits serve different functions.
(a) Reconstruction of L1-3 interneurons and L5 pyramidal neurons recorded simultaneously from an acute cortical slice. The double colored dots indicate the putative synaptic contacts. The schematic drawing shows symbolically the synaptic connections and dendritic recording sites.
(b–d) The effects of continuous (in L1 interneurons) or brief (in L2/3 interneurons) depolarizing current injections on the complex dendritic complex spikes evoked by simultaneous near-threshold current injections from the dendritic and somatic recording electrodes in the shape of an EPSP. Scale bars apply to all recording traces in b–d with 80 mV and 2 mV bars applied to traces with and without action potentials, respectively. Note the reduced number of somatic action potentials after activation of L2/3 interneurons (NBefore: 2.3±0.1; NAfter: 1.0±0.0, n=19;Z=4.0; p<0.005; Wilcoxon test) and NGC firing-evoked spikelets in ENGC.
(e) The incidences of dendritic complex spikes after current injections in L1-3 interneurons. Values for the incidences in SBC (Iinj in L5P: 56.9±6.6%; Iinj in L2/3I and L5P: 1.4±1.3%; Z=2.7; Iinj in SBC, L2/3I and L5P: 70.8±6.3%; Z=2.0; n=9), and ENGC (Iinj in L5P: 62.5±5.3%; Iinj in ENGC and L5P: 13.8±5.1%; Z=2.9; Iinj in L2/3I and L5P; Z=2.8: 2.5±1.7%; Iinj in ENGC, L2/3I and L5P: 0.0±0.0%; Z=2.8; n=10) interneuronal circuits. Note larger uIPSPs induced by the synchronized firing in ENGCs and their targeting L2/3 interneurons (recorded in L5 pyramidal neurons at resting membrane potentials) (ENGC↔L2/3I: 0.55±0.07 mV; ENGC: 0.25±0.04 mV; Z=2.8; L2/3I: 0.33±0.05 mV; Z=2.8; n=10, p<0.01; Wilcoxon tests). Asterisks indicate p<0.05 (Wilcoxon tests).