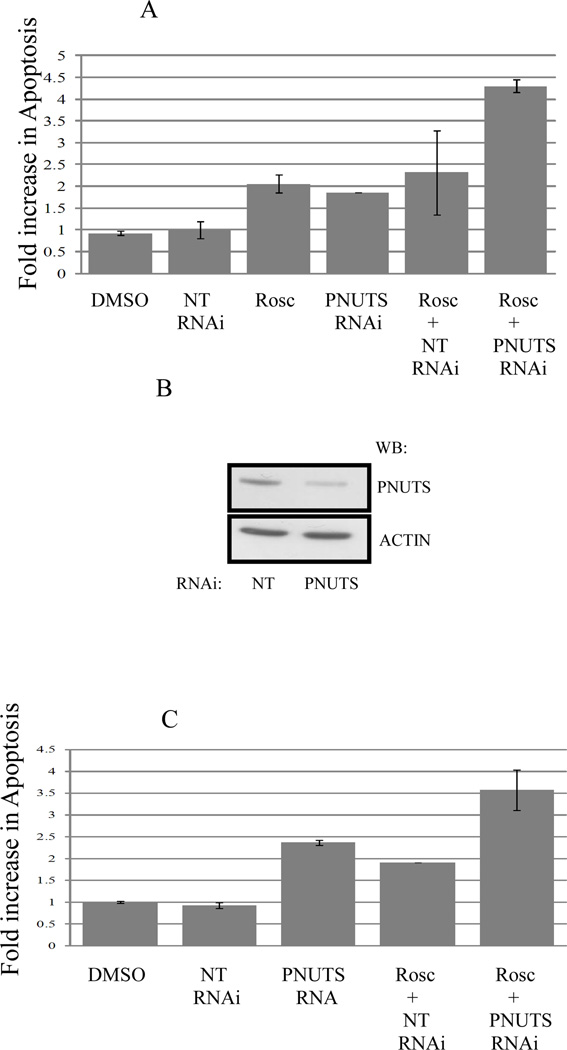
Figure 2. PNUTS knockdown increases the apoptotic effect of Roscovitine in cancer cells.
A. MCF7 cells were treated as control (DMSO or nontargeting RNA) or transfected with PNUTS RNAi or treated with Rosc or these treatments were combined as described in figure 1. Analysis was performed by TUNEL assay as described in the Materials and Methods. The amount of apoptosis detected in control cells (DMSO) was normalized to one. The graph depicts the fold increase in degraded DNA observed in the cells under each condition. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean of triplicate samples and data shown is representative of two independent experiments. B. PNUTS knockdown and equal loading were confirmed in MCF7 cells by examining expression of PNUTS and β-actin, respectively. The antibodies utilized are indicated to the right of the figure. C. Following treatment of p53−/− HCT116 cells as described in figure 1, apoptosis was measured by a Cell Death Detection ELISA (Roche Diagnostics) which detects degraded DNA released from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. The amount of apoptosis (degraded DNA) detected in control DMSO treated cells was normalized to one. The graph depicts the fold increase in degraded DNA observed due to PNUTS RNAi. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean of triplicate samples and data shown is representative of two independent experiments.