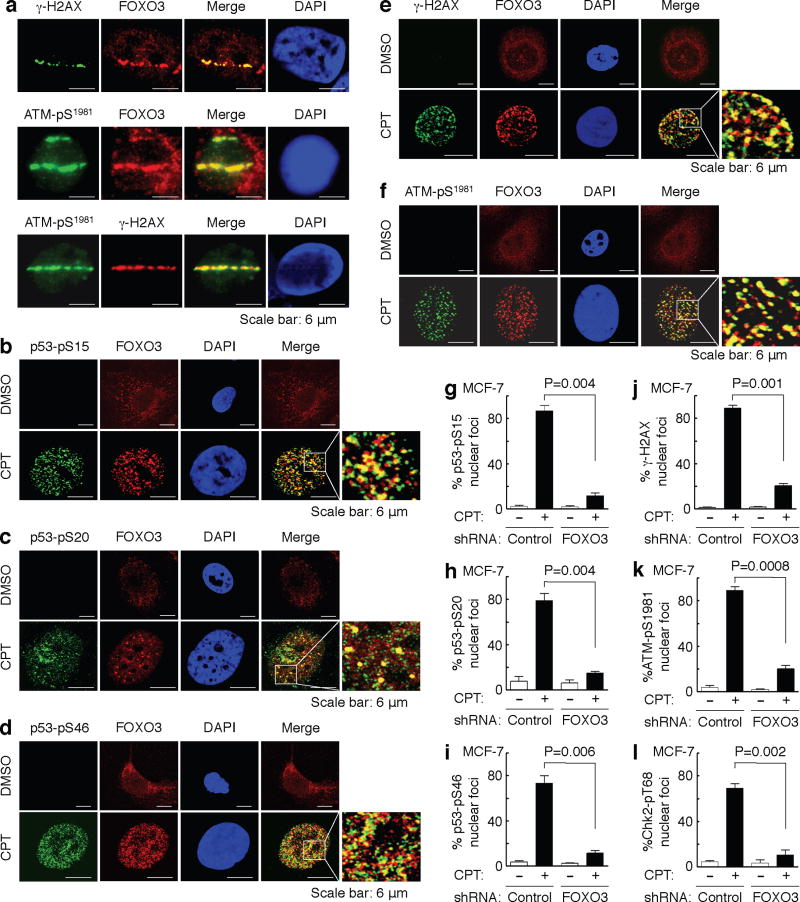
Fig. 2. FOXO3 is essential for the formation of ATM-Chk2-p53-H2AX nuclear foci.
(a) Accumulation of a fraction of FOXO3 at laser-induced damage was detected in MCF-7 cells 30 min after focused laser micro-irradiation. The cells were stained with Abs against FOXO3 and γ-H2AX or ATM-pS1981, followed by fluorescence microscopy as described in the section of Immunofluorescence under “Methods”. DAPI was used to show the nuclei, and co-localizations of FOXO3 with ATM-pS1981 were shown as the merged images. Scale bar: 6 μm. (b–f) MCF-7 cells were treated with CPT (1 μM) or DMSO control for 2 h, and co-localizations between FOXO3 and p53-pS15 (b) or p53-pS20 (c) or p53-pS46 (d) or γ-H2AX (e) or ATM-pS1981 (f) were detected using Abs as indicated and followed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar: 6 μm. (g–l) FOXO3 is necessary for the formation of p53-pS15, p53-pS20, and p53-pS46, γ-H2AX, ATM-pS1981, and Chk2-pT68 nuclear foci upon CPT-induced DNA damage. MCF-7 stable cell lines transfected with FOXO3-shRNA or control-shRNA were treated with CPT (1 μM) or DMSO for 2 h, and then the subcellular localizations and co-localization of FOXO3 and p53-pS15 (g) or p53-pS20 (h) or p53-pS46 (i) or γ-H2AX (j) or ATM-pS1981 (k) or Chk2-pT68 (l) were detected using specific Abs as indicated. An average of 200 cells with specific nuclear foci in each comparison was determined and shown. The images of nuclear foci of these proteins were shown in Supplementary Fig. S5. The error bars represent standard deviation, and the statistical test is the paired t-test.