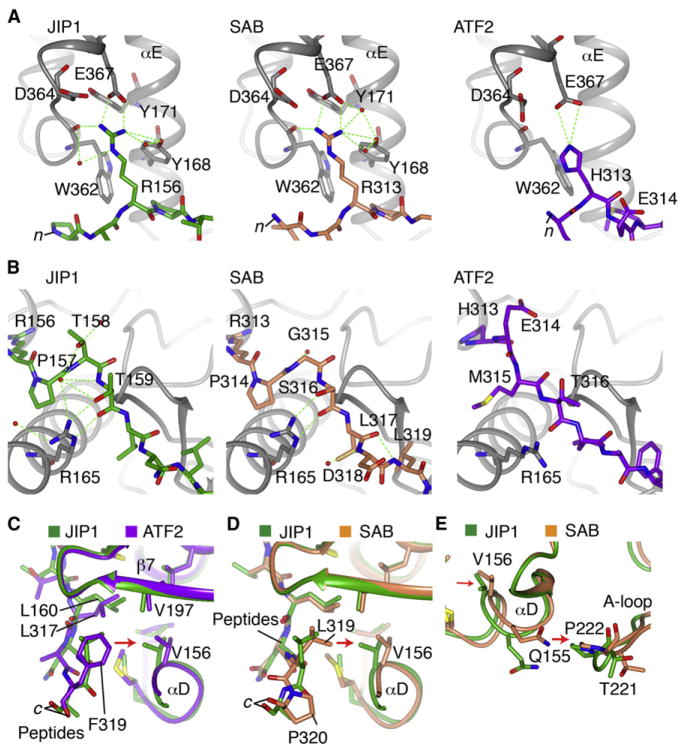
Figure 3. Structural Features of Peptide Specificity.
(A) Hydrogen bonding in the n terminus of the peptides. JNK3 is gray and the peptides, JIP1, SAB, and ATF2 are differently colored.
(B) Differences in binding to JNK3 in the middle of the peptides.
(C) Comparison of the c terminus of JIP1 and ATF2 peptide binding. The Phe residue in ATF2 extends further toward αD and shifts its positioning relative to the JIP1-bound structure.
(D) Comparison of the c terminus of JIP1 and SAB peptide binding. The c-terminal P350 in SAB enforces an altered position of the peptide backbone for the adjacent L349, which is transmitted to a shift in αD.
(E) The shift in αD induced by SAB is transmitted to the adjacent P222 in the A-loop, similar to the ATF2 induced shift (not shown).
See also Figure S3.