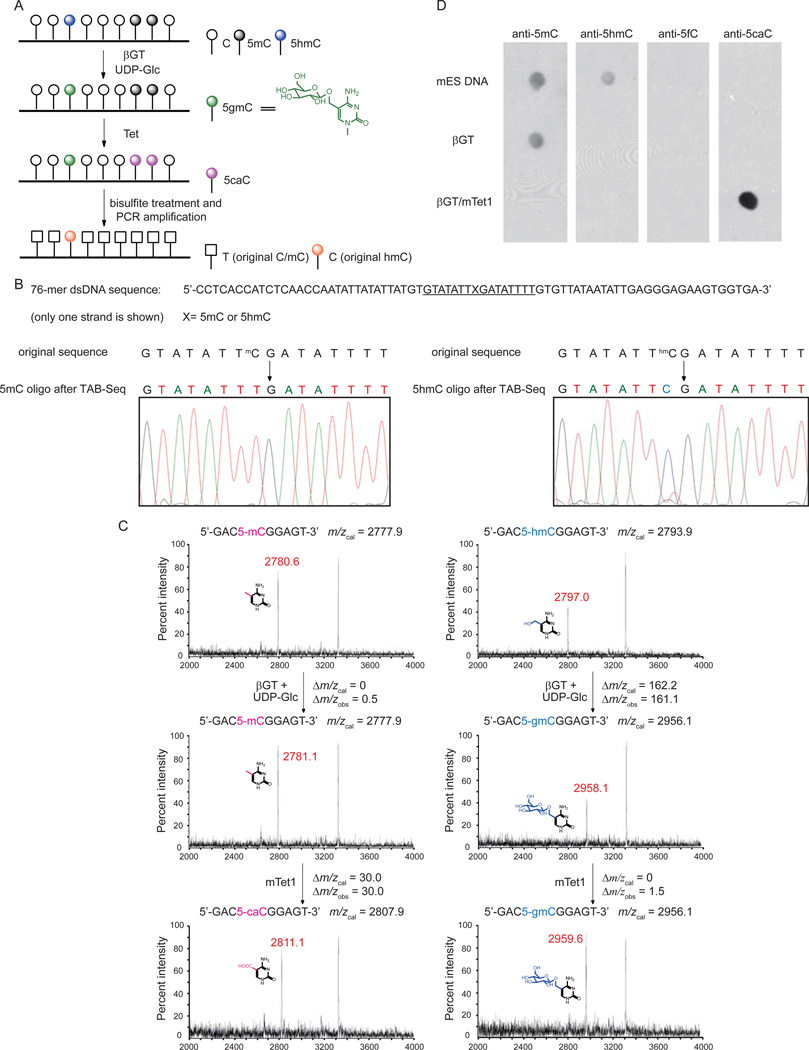
Figure 1. TAB-Seq Strategy and Validation.
(A)Schematic diagram of TAB-Seq. 5 hmCs in genomic DNA are protected by glucosylation, and then 5mCs are converted to 5caCs by Tet-mediated oxidation. After bisulfite treatment, both 5caC (generated from 5mC) and C display as T while 5gmC (generated from original 5hmC) displays as C.
(B) TAB-Seq of 76-mer dsDNA with 5mC or 5hmC. The 76-mer dsDNA with 5mC (left) or 5hmC (right) modification was subject to TAB-Seq as described in Figure 1A. Sanger sequencing results showed that 5mC was completely converted to T (left) and 5hmC still read as C (right).
(C) Mass spectrometry characterization of the products from TAB-Seq with a model DNA. The dsDNA contains a 5mC (left) or 5hmC (right) on a 9mer strand annealed to a 11mer complementary strand. The DNA was subject to βGT-mediated glucosylation and mTet1-mediated oxidation. The reactions were monitored by MALDI-TOF/TOF with the calculated and observed molecular weight indicated.
(D)Validation of 5mC and 5hmC conversion in genomic DNA (mouse ES) with western blotting. The untreated DNA, βGT-treated DNA, and βGT/mTet1-treated DNA were tested with dot blot assays using antibodies against 5mC, 5hmC, 5fC and 5caC, respectively. No 5hmC could be observed after glucosylation. Almost all 5mCs were converted into 5caCs after the mTet1-mediated oxidation.
See also Figure S1.