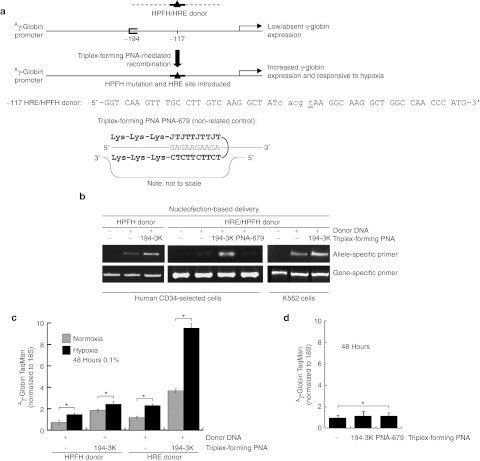
Figure 3.
Triplex-forming PNAs can mediate recombination of the HPFH donors in hematopoietic CD34-selected cells. (a) Human CD34+ cells were mock transfected or transfected with triplex-forming PNA γ-194-3K and one of two donors: −117 HRE/HPFH donor, which contains a HPFH mutation at −117 as well as the consensus HRE sequence, or as a control, a −117 HPFH donor, which contains a HPFH mutation at −117 but no HRE consensus sequence. (b) Allele-specific PCR of the genomic DNA from treated CD34-selected cells or K562 cells revealed the presence of the −117 HPFH mutation in cells treated with the −117 HRE/HPFH donor or the control −117 HPFH donor, in conjunction with triplex-forming PNA γ-194-3K, but not in conjunction with a non-related control triplex-forming PNA PNA-679, indicating targeted and specific gene conversion at the −117 site. Oligonucleotides were introduced into human CD34+ cells by nucleofection delivery. (c) CD34-selected cell samples (three independent replicates for each sample, *P < 0.05) treated with triplex-forming PNA γ-194-3K and either −117 HRE/HPFH donor DNA or control −117 HPFH donor, were subjected to hypoxia for 48 hours. RNA was then harvested from these hypoxia-treated cells and from a normoxia set for comparison. qRT-PCR with TaqMan probes demonstrated that γ-globin expression in triplex-forming PNA γ-194-3K and −117 HRE/HPFH donor DNA-treated cells were now responsive to hypoxia. In contrast, cells treated with triplex-forming PNA γ-194-3K and control −117 HPFH donor did not show hypoxia-based regulation of γ-globin expression. (d) CD34-selected cell samples (three independent replicates for each sample, *P < 0.05) were mock transfected or transfected with triplex-forming PNA γ-194-3K or a non-related control triplex-forming PNA PNA-679, and RNA was harvested. qRT-PCR indicated that neither triplex-forming PNA γ-194-3K nor a non-related control triplex-forming PNA (PNA-679) induced γ-globin expression by themselves. HPFH, hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin; HRE, hypoxia-responsive element; PNA, peptide nucleic acid; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR.