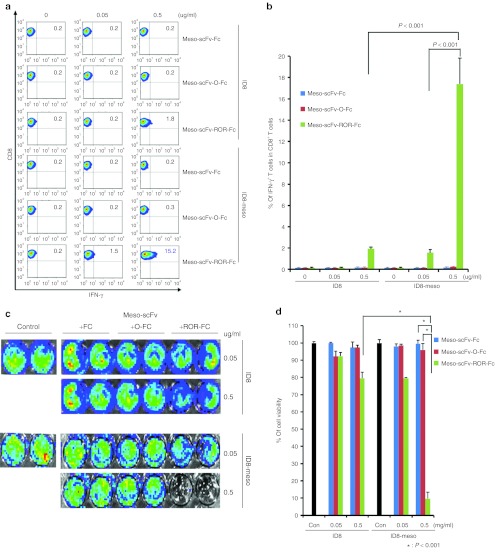
Figure 2.
Major histocompatibility complex class I presentation of ovalbumin (OVA) peptide to OVA-specific CD8+T cells by ID8-meso cells treated with Meso-scFv-ROR-Fc. (a) Flow cytometry characterization of OVA-specific CD8+ T-cell activation by ID8-meso cells treated with different chimeric proteins. ID8-meso or control ID8 tumor cells were incubated with different protein concentrations followed by incubation with 2 × 105 OVA-specific cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes (CTLs). OVA-specific CD8+ T-cell activation was determined by CD8 and intracellular interferon γ (IFN-γ) staining. (b) Representative bar graph depicting the % of IFN-γ-secreting OVA-specific CD8+ T cells out of total OVA-specific T cells (mean ± SD). (c) Representative luminescence imaging of in vitro OVA-specific CTL killing of luciferase-expressing ID8-meso cells treated with different concentrations of Meso-scFv-ROR-Fc. Luciferase-expressing ID8-meso or control ID8 tumor cells treated with chimeric proteins were later incubated with 2 × 105 OVA-specific CD8+ T cells. CTL-mediated tumor cell death was determined by decreasing luminescence activity. (d) Bar graph depiction of tumor cell viability after treatment with protein and/or OVA-specific cytotoxic T cells (mean ± SD) (data representative of two experiments). Meso-scFv, mesothelin single-chain variable fragment.