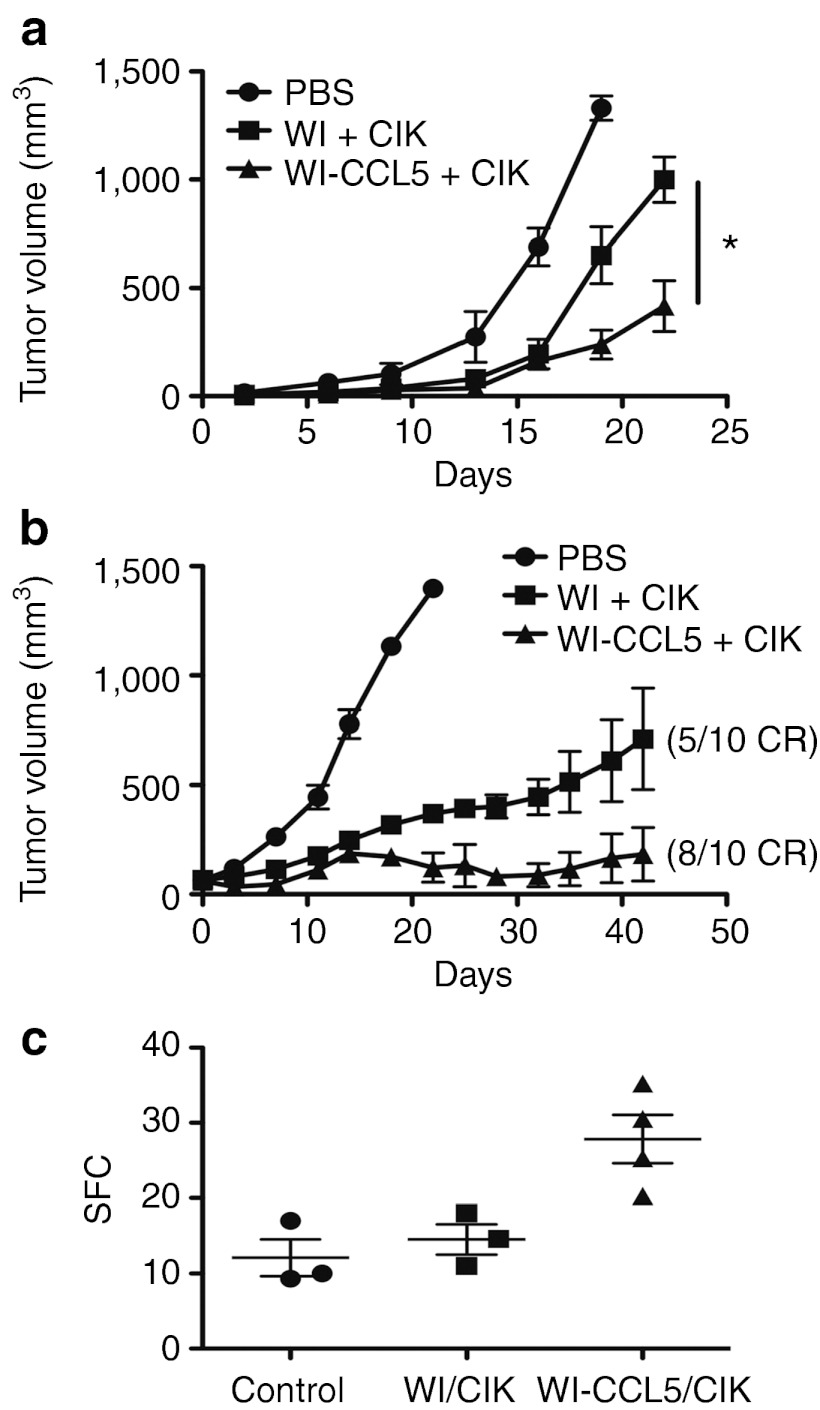
Figure 6.
CCL5 expression demonstrates therapeutic and immunotherapeutic advantages in immune-competent mice. (a) Mice (4T1-bearing BALB/c) were treated with 1 × 107 CIK cells pre-infected with the same viruses as before (n = 8 per group) and antitumor effects determined by caliper measurement over time (WI-CCL5/CIK performed significantly better than all other treatments (*P < 0.05) at all times after day 15). (b) In a repeat experiment, MC38 tumor-bearing C57/BL6 mice were treated as before (n = 10) and tumor growth followed. (c) In a satellite experiment, mice were killed 3 days after treatment (n = 4/group), and the level of T-cell response targeting tumor antigens was determined by IFN-γ ELISPOT. The CCL5 expression leads to a significant increase in the level of early immune activation (P = 0.024). CIK, cytokine-induced killer; IFN, interferon; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; SFC, spot-forming cells.