Abstract
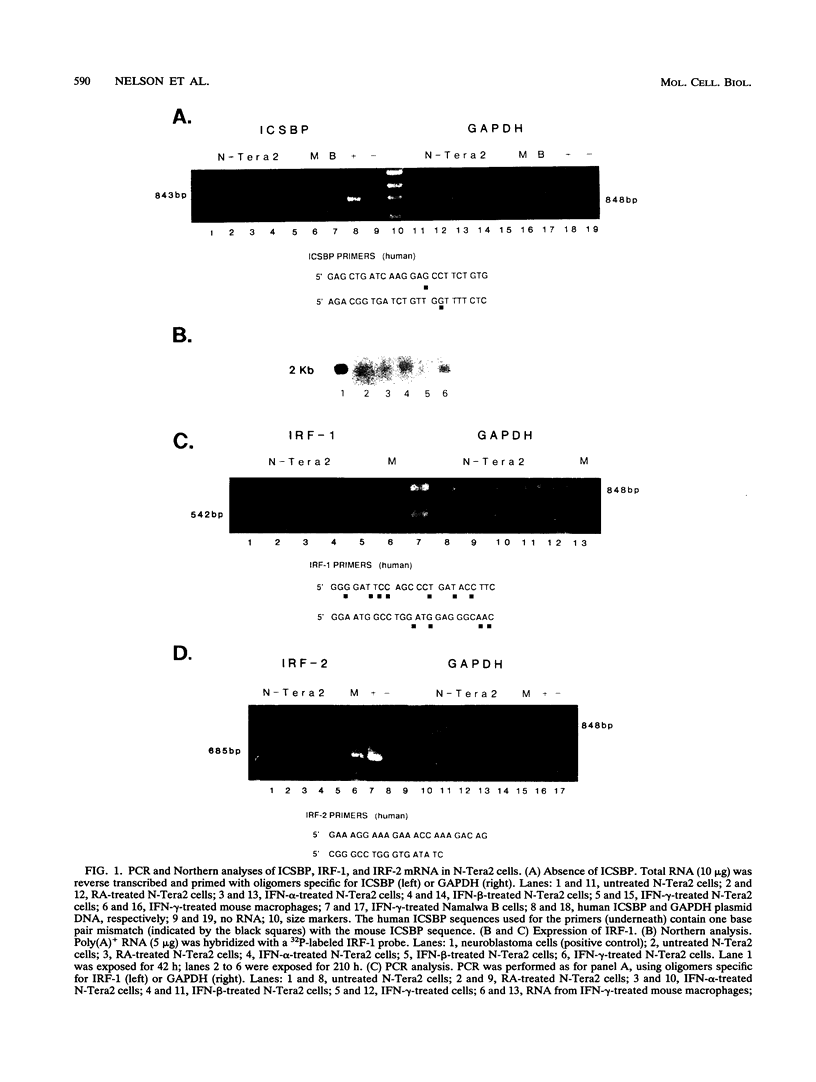
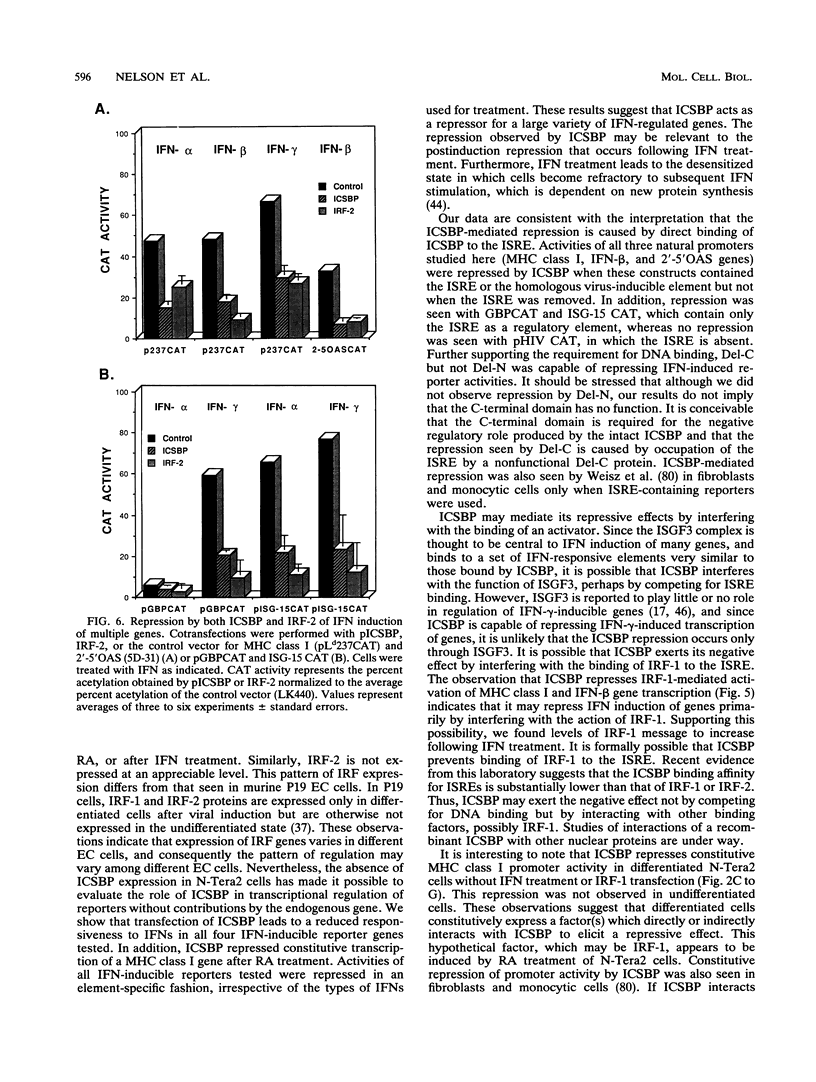
We previously isolated a cDNA clone encoding interferon consensus sequence-binding protein (ICSBP), a member of the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) family, that binds to the interferon (IFN)-stimulated response element (ISRE) of many IFN-regulated genes. In this investigation, we studied the functional role of ICSBP by transient cotransfection of ICSBP cDNA with IFN-responsive reporter genes into the human embryonal carcinoma cell line N-Tera2. These cells were shown not to express ICSBP or IRF-2, thus allowing functional analysis of transfected cDNAs. Cotransfection of ICSBP into cells treated with retinoic acid or any of the IFNs (alpha, beta, or gamma) repressed expression of a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter driven by the major histocompatibility complex class I gene promoter. Similarly, ICSBP repressed expression of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporters driven by the ISREs of the 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase, guanylate-binding protein, and ISG-15 genes in IFN-treated cells. The repression was dependent on the presence of the ISRE in the reporter. Deletion analysis showed that the putative N-terminal DNA binding domain of ICSBP by itself is capable of mediating the repression. Using the same cotransfection conditions as for ICSBP, a similar repression of these reporters was observed with IRF-2. Finally, ICSBP repressed the IRF-1-mediated induction of major histocompatibility complex class I and IFN-beta reporters in the absence of IFN or retinoic acid. Taken together, these results suggest that ICSBP is a negative regulatory factor capable of repressing transcription of target genes induced by IFN, retinoic acid, or IRF-1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaldi I., Reith W., Berte C., Mach B. Induction of HLA class II genes by IFN-gamma is transcriptional and requires a trans-acting protein. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):999–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. W. Retinoic acid induces neuronal differentiation of a cloned human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. W., Trinchieri G., Perussia B., Baglioni C. Induction of class I major histocompatibility complex antigens in human teratocarcinoma cells by interferon without induction of differentiation, growth inhibition, or resistance to viral infection. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):740–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcari P., Martinelli R., Salvatore F. The complete sequence of a full length cDNA for human liver glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: evidence for multiple mRNA species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):9179–9189. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.9179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Archibald A. L., Kvist S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the murine H-2Kk gene. Comparison of three H-2K locus alleles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9473–9487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artzt K., Jacob F. Letter: Absence of serologically detectable H-2 on primitive teratocarcinoma cells in culture. Transplantation. 1974 Jun;17(6):632–634. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197406000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay S. K., Kalvakolanu D. V., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons: functional complementation between trans-acting factors induced by alpha interferon and gamma interferon. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5055–5063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. P., Randle B. J., Burke D. C. Interferon synthesis in the early post-implantation mouse embryo. Differentiation. 1984;27(3):229–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Vigneron M., Peretz D., Revel M., Chebath J. Interferon-responsive regulatory elements in the promoter of the human 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4498–4504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Flavell R. A., Sharp P. A. A gamma-interferon-induced factor that binds the interferon response sequence of the MHC class I gene, H-2Kb. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1139–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke P. A., Ozato K. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Year Immunol. 1989;4:23–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Vaiman D., Chebath J. Enhancer functions and in vitro protein binding of native and mutated interferon-responsive sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1679–1695. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Rosen J. M., Guille M. J., Lewin A. R., Porter A. G., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Overlapping sites for constitutive and induced DNA binding factors involved in interferon-stimulated transcription. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):831–839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Watine B., Israël A., Kourilsky P. The regulation and expression of MHC class I genes. Immunol Today. 1990 Aug;11(8):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90114-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Darnell J. E., Jr Two distinct alpha-interferon-dependent signal transduction pathways may contribute to activation of transcription of the guanylate-binding protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5147–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey A., Thornton A. M., Lonergan M., Weissman S. M., Chamberlain J. W., Ozato K. Occupancy of upstream regulatory sites in vivo coincides with major histocompatibility complex class I gene expression in mouse tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3590–3599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Elenbaas B. A., An J. B., Lee I. J., Ozato K. Two upstream elements activate transcription of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2533–2540. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Holmes J., Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Beckmann M. P., Park L. S., Schooley K. A., Coffman R. L., Mosmann T. R., Paul W. E. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Murata M., Burke P. A., Shirayoshi Y., Appella E., Sharp P. A., Ozato K. Negative regulation of the major histocompatibility complex class I promoter in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3145–3149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. K., Lehman J. M. Control of beta-interferon expression in murine embryonal carcinoma F9 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3553–3556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Kessler D. S., Veals S. A., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8555–8559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kimura Y., Miyamoto M., Barsoumian E. L., Taniguchi T. Induction of endogenous IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes by a regulatory transcription factor, IRF-1. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):270–272. doi: 10.1038/337270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Hammer J., Taniguchi T. Involvement of a cis-element that binds an H2TF-1/NF kappa B like factor(s) in the virus-induced interferon-beta gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3335–3346. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ohno S., Yasumitsu H., Taniguchi T. Delimitation and properties of DNA sequences required for the regulated expression of human interferon-beta gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Hotta H., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Interferon-beta gene regulation: tandemly repeated sequences of a synthetic 6 bp oligomer function as a virus-inducible enhancer. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Willison K., Sakakibara J., Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Absence of the type I IFN system in EC cells: transcriptional activator (IRF-1) and repressor (IRF-2) genes are developmentally regulated. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh S., Harada H., Fujita T., Mimura T., Taniguchi T. Sequence of a cDNA coding for human IRF-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8372–8372. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification and characterization of a novel repressor of beta-interferon gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):868–879. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification of an inducible factor that binds to a positive regulatory element of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3309–3313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. The control of interferon-inducible gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80802-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
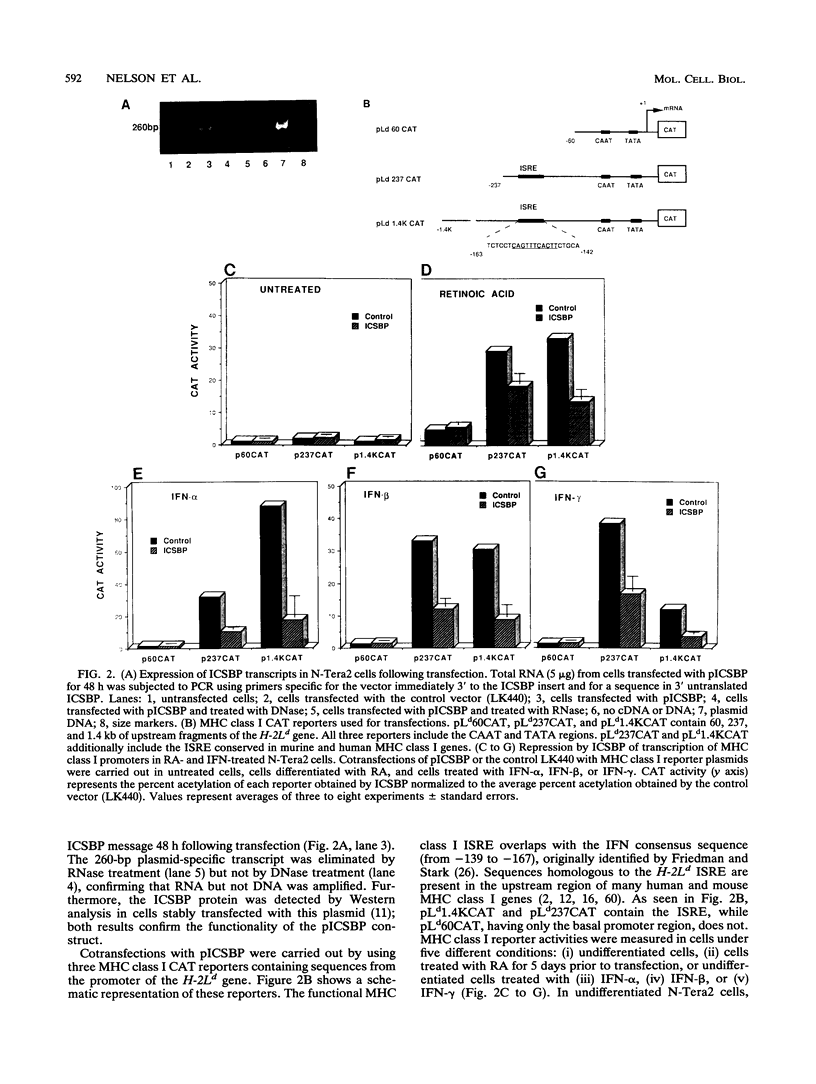
- Landolfo S., Gariglio M., Gribaudo G., Jemma C., Giovarelli M., Cavallo G. Interferon-gamma is not an antiviral, but a growth-promoting factor for T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):503–509. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Chaudhuri A., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction by interferon. New protein(s) determine the extent and length of the induction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lew D. J., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Synergistic interaction between interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma through induced synthesis of one subunit of the transcription factor ISGF3. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent transcriptional activation: signal transduction without second messenger involvement? New Biol. 1990 Oct;2(10):923–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Decker T., Strehlow I., Darnell J. E. Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Janeway C. A., Jr Interferon gamma plays a critical role in induced cell death of effector T cell: a possible third mechanism of self-tolerance. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1735–1739. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh J. E., Chang C. H., Fodor W. L., Flavell R. A. Dissection of the interferon gamma-MHC class II signal transduction pathway reveals that type I and type II interferon systems share common signalling component(s). EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1351–1363. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Unkeless J. C., Ravetch J. V. Gamma-interferon transcriptionally regulates an early-response gene containing homology to platelet proteins. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):672–676. doi: 10.1038/315672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald N. J., Kuhl D., Maguire D., Näf D., Gallant P., Goswamy A., Hug H., Büeler H., Chaturvedi M., de la Fuente J. Different pathways mediate virus inducibility of the human IFN-alpha 1 and IFN-beta genes. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90091-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraskovsky E., Chen W. F., Shortman K. IL-2 and IFN-gamma are two necessary lymphokines in the development of cytolytic T cells. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1210–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Sequence of a cDNA coding for human IRF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3292–3292. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Decker T., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon induction of gene transcription analyzed by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- N'Guyen C., Sodoyer R., Trucy J., Strachan T., Jordan B. R. The HLA-AW24 gene: sequence, surroundings and comparison with the HLA-A2 and HLA-A3 genes. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(5):479–489. doi: 10.1007/BF00430931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Segars J. H., Levi B. Z., Ozato K. Retinoic acid-dependent transactivation of major histocompatibility complex class I promoters by the nuclear hormone receptor H-2RIIBP in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):937–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., John J., Shearer M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Use of a selectable marker regulated by alpha interferon to obtain mutations in the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4605–4612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politis A. D., Sivo J., Driggers P. H., Ozato K., Vogel S. N. Modulation of interferon consensus sequence binding protein mRNA in murine peritoneal macrophages. Induction by IFN-gamma and down-regulation by IFN-alpha, dexamethasone, and protein kinase inhibitors. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):801–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. E., Brasnett A. H., Gilbert C. S., Porter A. C., Gewert D. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. F., Harada H., Wolchok J. D., Taniguchi T., Vilcek J. Critical role of a common transcription factor, IRF-1, in the regulation of IFN-beta and IFN-inducible genes. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):185–193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford M. N., Hannigan G. E., Williams B. R. Interferon-induced binding of nuclear factors to promoter elements of the 2-5A synthetase gene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):751–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Dierks P., Ragg H., Weissmann C. A 46-nucleotide promoter segment from an IFN-alpha gene renders an unrelated promoter inducible by virus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Lengyel P. The interferon system. A bird's eye view of its biochemistry. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5017–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Burke P. A., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferon-induced transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene accompanies binding of inducible nuclear factors to the interferon consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5884–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D., Shultz L. D., Gray P. W., Johnson H. M. Gamma-interferon is one of several direct B cell-maturing lymphokines. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):801–804. doi: 10.1038/309801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferons increase transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene via a 5' interferon consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2625–2630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Feinman R., Vilcek J. Differential effects of type I IFN and IFN-gamma on the binding of tumor necrosis factor to receptors in two human cell lines. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2272–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veals S. A., Schindler C., Leonard D., Fu X. Y., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr, Levy D. E. Subunit of an alpha-interferon-responsive transcription factor is related to interferon regulatory factor and Myb families of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3315–3324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan Y. J., Orrison B. M., Lieberman R., Lazarovici P., Ozato K. Induction of major histocompatibility class I antigens by interferons in undifferentiated F9 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Feb;130(2):276–283. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. M., Farber J. M. 5' regulatory region of a novel cytokine gene mediates selective activation by interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):417–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan C., Tamm I. Molecular cloning and characterization of interferon alpha/beta response element binding factors of the murine (2'-5')oligoadenylate synthetase ME-12 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]