Figure 3.
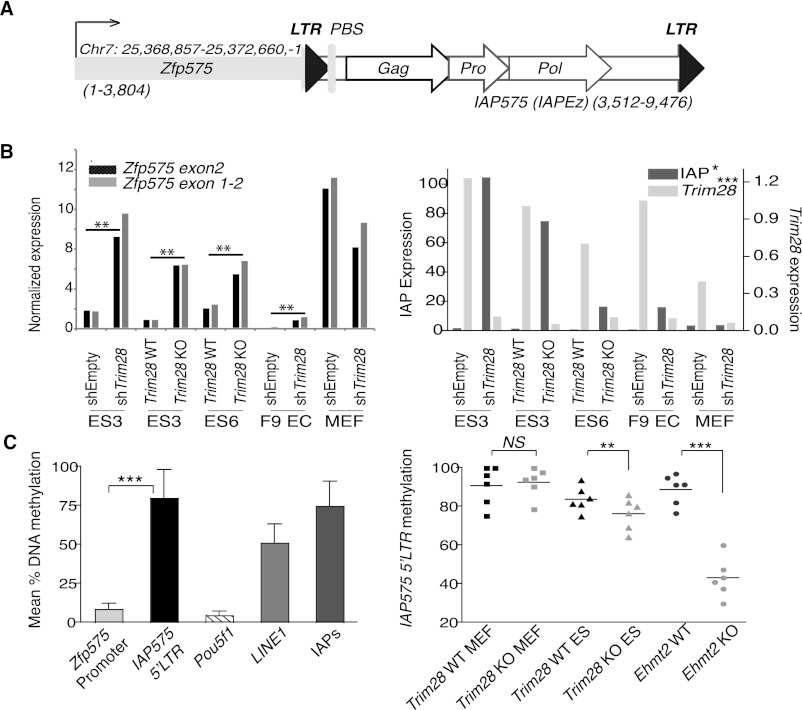
Expression and cytosine methylation at the Zfp575 gene and adjacent IAP. (A) Map (drawn to scale) of the Zfp575 gene that just overlaps a full-length IAP (named IAP575 and of the IAPEz type) with both gene and IAP in the same orientation (sizes of each are stated). (LTR) Long terminal repeat; (PBS) primer binding site; (Gag) group-specific antigen; (Pro) protease; (Pol) polymerase. (B) TRIM28 knock-out and knockdown (comparing control, shEmpty and KD, shTRIM28) cell lines were assessed for their expression of Zfp575 (left panel) using two different primer sets, or TRIM28 or IAPs as controls (right panel). Unpaired t-tests were used to compare controls with TRIM28-depleted samples for all ES and EC cell lines: Zfp575, P = 0.0015; IAP, P = 0.0344; TRIM28, P = 0.0008. Since Zfp575 is normally expressed specifically in brain, we also verified it to be expressed in primary neurospheres and brain (data not shown). (C) Quantitative pyrosequencing was used to measure DNA methylation levels at the Zfp575 promoter versus the flanking 5′-LTR IAP575 promoter (left panel). Control primers were specific for the Pou5f1 promoter or global LINE1s or global IAP LTRs (IAPs). Bars represent means over multiple CpG positions with error bars showing the SD across all CpGs. (Right panel) Samples were compared (across six CpG positions) for their methylation levels at the IAP575 promoter. Primordial germ cells were also used to show that IAP575 is demethylated in germ cells to a level not much lower than in Trim28-deleted ES cells (e.g., to an average of 69% instead of 76%) (data not shown). Two-tailed paired t-tests display all significant differences: Trim28 WT versus KO ES, P = 0.0088; Ehmt2 WT versus KO, P = 0.0001.