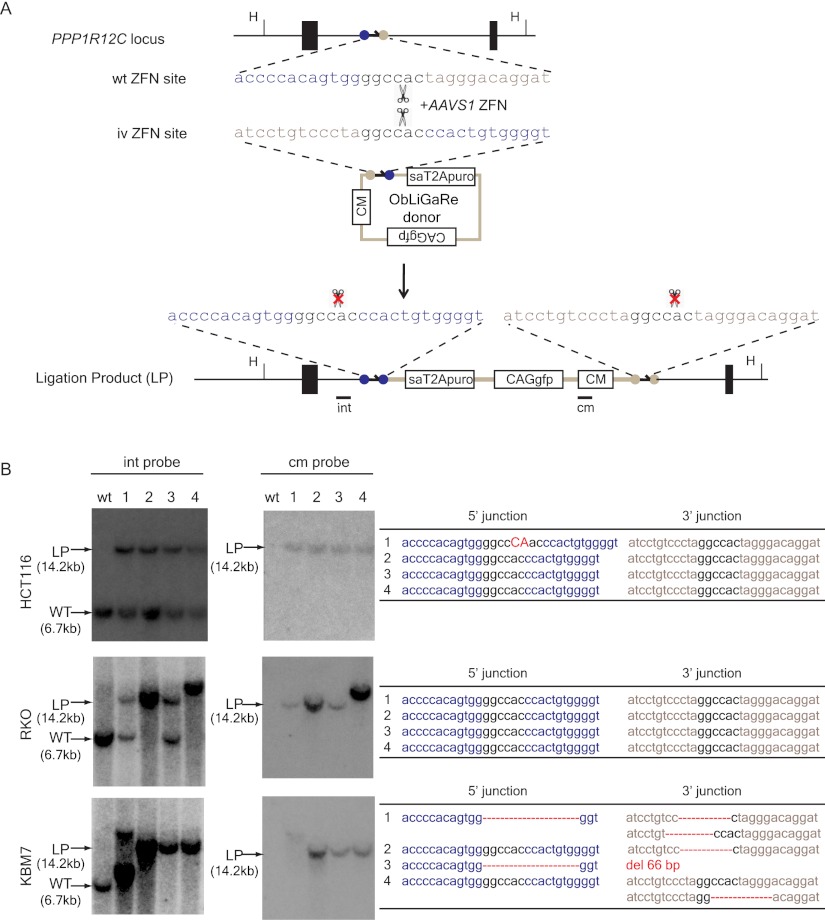
Figure 1.
ObLiGaRe at the AAVS1 locus. (A) Schematic illustration of the ObLiGaRe strategy. ZFN recognition sites are indicated as gray and blue circles with the corresponding sequences displayed in the same color scheme. The predicted joining sequences between the vector and the genome are shown. The insertion of the vector in the AAVS1 locus will cause a size shift from 6.7 kb (wild type [WT]) to 14.2 kb (ligation product [LP]) of a HindIII (H) digested fragment. AAVS1 internal (int) and vector-specific (cm) probes are indicated in the map at the hybridization sites. (B) Southern blot of four puro-resistant colonies after ObLiGaRe at AAVS1 locus in HCT116 (upper), RKO (middle), and KBM-7 (lower) with int probe (left) and cm probe (right) with sequences at the 5′ and 3′ junctions corresponding to each clone listed on the right. (Red) Insertions; (red dotted lines) deletions. (sa) Splicing acceptor; (CM) chloramphenicol-resistant marker.