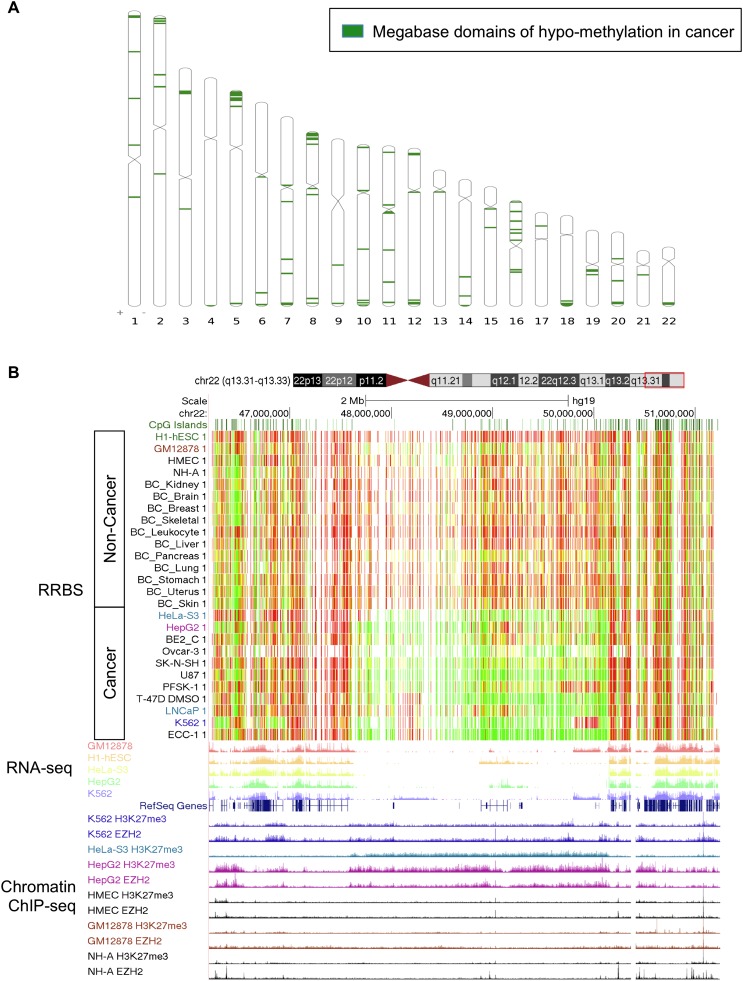
Figure 2.
Megabase-size domains are hypomethylated across cancers. (A) We identified 114 megabase windows in the genome that are significantly hypomethylated across cancer cell lines, compared to primary cell lines and tissues. These domains are enriched near the ends and centromeres of chromosomes. (B) UCSC Genome Browser visualization of a 2-Mb hypomethylated domain on the q-arm of chromosome 22. The color in the RRBS track indicates the percent of molecules that are methylated at each CpG position. (Red) 100%, (yellow) 50%, (green) 0%. Hypomethylation across cancers occurs in the 2-Mb gene-depleted region. RNA-seq demonstrates that the methylated regions flanking the cancer-specific hypomethylated domain contain genes that are expressed in both the cancer (HeLa, HepG2, and K562) and noncancer samples (GM12878 and H1-HESC). The chromatin ChIP-seq tracks demonstrate that the hypomethylated region is marked by cancer-specific repressive H3K27me3 and EZH2 binding (cancer = K562, HeLa, HepG2; noncancer = HMEC, GM12878, NH-A).