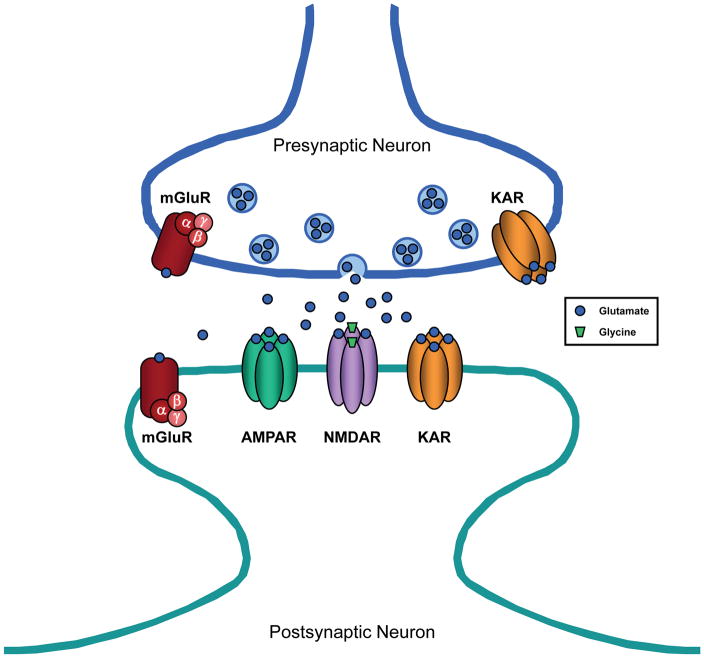
Figure 1.
Excitatory synapse in the CNS. The excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate, is released from presynaptic vesicles and diffuses across the synaptic cleft to act on two different types of receptors: ionotropic glutamate receptors, which have an intrinsic ion channel, and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR), which are coupled to G proteins (α, β, and γ subunits). The three subtypes of ionotropic glutamate receptors include AMPA receptor (AMPAR), NMDA receptor (NMDAR), and kainate receptor (KAR).