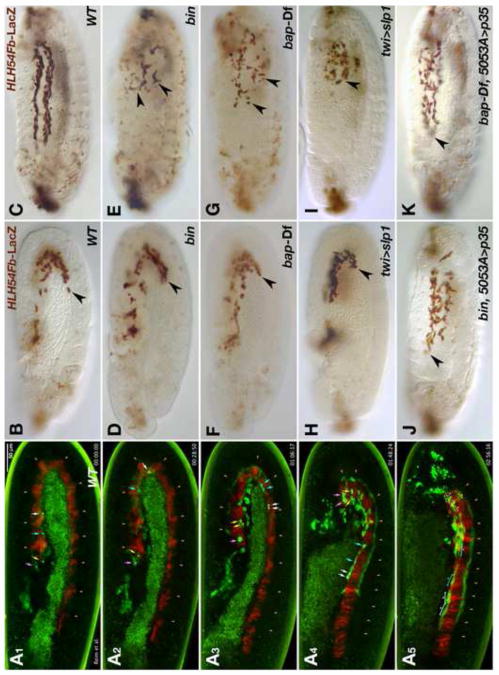
Fig. 1. Normal migration of longitudinal visceral muscle founders in the wild type and disrupted migration and survival in the absence of trunk visceral mesoderm.
(A) Still images of wild type embryo from Movie 1 at five different time points (A1: 0 min; A2: 29 min, A3: 1 h 6 min, A4: 1 h 48 min, A5: 2 h 56 min). The embryo carries HLH54F-GFP, which marks the CVM and migrating LVM founders (green), as well as bap3-RFP, which marks the trunk visceral mesoderm (red; parasegmental borders marked by arrow heads). Four migrating LVM progenitors and their daughter cells are marked by color-coded arrows and the syncytia formed from these by brackets. (B – K) Embryos carrying HLH54Fb-lacZ are stained with anti-β-galactosidase (β-gal) antibodies at stage 11 (B, D, F, H• and late stage 13 (C, E, G, I-K). Shown are lateral views with the anterior on the left. (B) Wild type (WT) stage 11 control embryo. LacZ-positive LVM founder cells have left the posterior tip of the extended germ band and migrate around the U-turn toward the anterior on either side of the embryo. (C) At the end of stage 13 the leading cells from the migration paths along the dorsal and ventral edges of the TVM have reached the anterior of the trunk. (D, E) show bin22 and (F, G) bap null (Df(3R)e-D7, tin-re28) mutant embryos at corresponding stages. Early migration of the CVM is largely unaffected in these mutants. At stage 13, the most anterior cells have failed to migrate beyond the point reached already during stage 11 (arrow heads) and are scattered within in the posterior third of the embryo. They are also reduced in number, and many of the remaining LacZ-positive cells feature abnormal cell shapes and have shrunken in size. Similar defects are observed upon ectopic activation of slp1 via twi-GAL4 (H, I), which blocks TVM formation. (J, K) If cell death is prevented by expression of the caspase inhibitor p35 within LVM founders, the cells survive and regain their ability to migrate, albeit less orderly, into the anterior trunk in bin or bap mutant backgrounds.