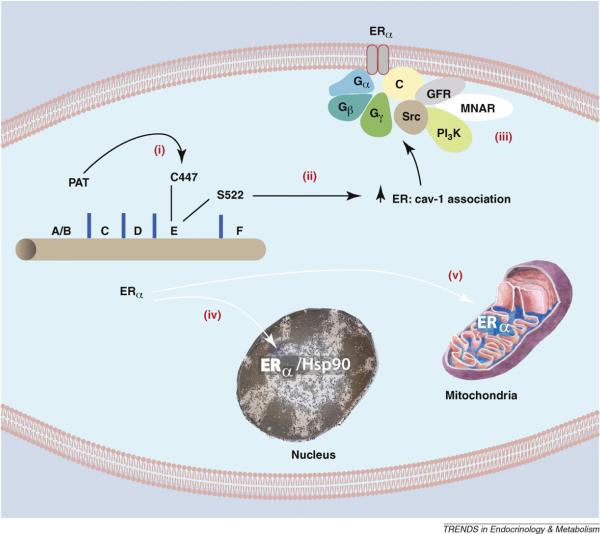
Figure 1.
Palmitoylation of Cysteine 447 is required for ERα translocation to the cell membrane. (i) Cysteine 447 in the E (ligand binding) domain of human ERα is the site of palmitoylation by an undetermined palmitoylacyltransferase (PAT). Palmitoylation of this amino acid is necessary for ERα association with (ii) caveolin-1 and subsequent transport to the membrane. Serine 522 also promotes the physical interaction of ER with caveolin-1 by unknown mechanisms. (iii) At the membrane, caveolin-1 serves as a scaffold for other signal molecules that are activated by E2 binding ERα in membrane caveolae rafts. Other ERα proteins are transported to the (iv) nucleus (chaperoned by heat shock protein 90 and dependent on a nuclear localization sequence), or to (v) mitochondria by an undetermined mechanism. GFR, growth factor receptor; MNAR, modulator of non-genomic action of the estrogen receptor; C, caveolin-1.