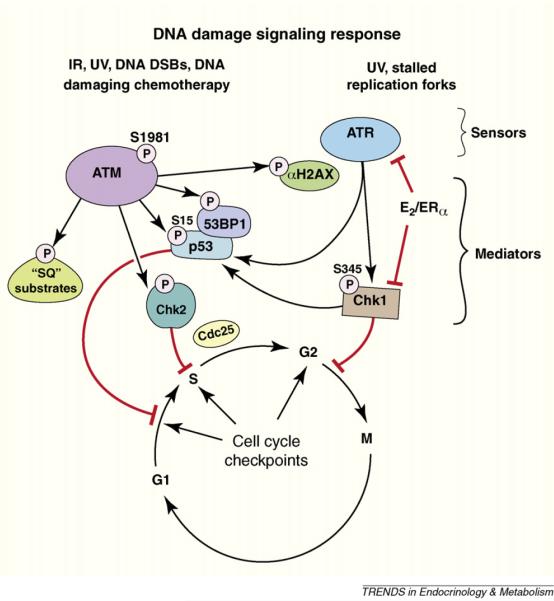
Figure 2.
Cartoon of response to DNA damage. Damage-causing double strand DNA breaks or replication fork stalling results in the assembly of unique repair protein complexes at the sites of the DNA lesions. The different complexes trigger activation of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) or ATM and Rad 3-related kinases (ATR), respectively, initiating signal transduction cascades. ATM and ATR phosphorylation of serine residues on checkpoint kinases (Chk) 1 and 2 mediates further signaling to enact cell cycle checkpoints. E2 acting through the cell membrane ERα stimulates AKT-induced block of ATR and Chk1 activity, leading to the inhibition of cell cycle checkpoints.