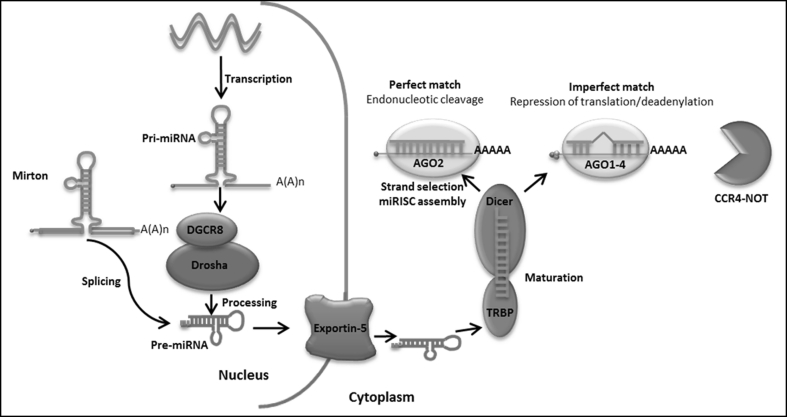
Fig. 1.
Figure depicting the production of mature miRNAs. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are encoded in the genome, their genes usually transcribed by RNA polymerase II. The transcripts undergo splicing and polyadenylation. The pri-miRNA is processed in the nucleus by the Drosha RNaseIII enzyme and the DGCR8 protein, producing the pre-miRNA. The pre-miRNA is exported to the cytoplasm by exportin-5 where Dicer and the TRBP cleave the pre-miRNA to yield a miRNA duplex (about 22-bp long). One strand is selected to function as a mature miRNA, the other strand is usually degraded. Mature miRNAs are then incorporated in a miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) that recognises and binds to the 3′ UTR of the target mRNA and represses translation (AGO-argonaute) [48]