Fig. 5.
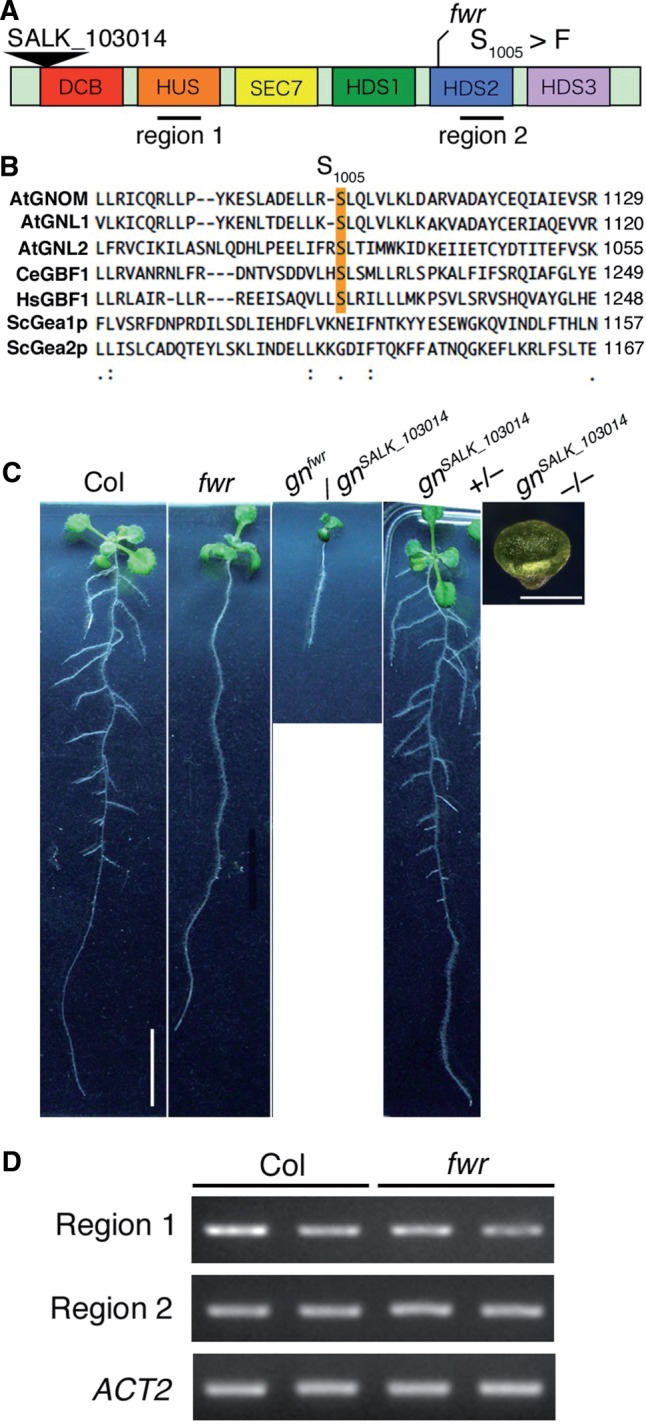
The FWR gene encodes GNOM protein. (A) Protein structure of GNOM (GN) and mutation point of fwr. GN has several characteristic domains: DCB, dimerization/cyclophilin-binding domain; HUS, homology upstream of Sec7 domain; Sec7, Sec7 domain; HDS, homology downstream of Sec7 domain. fwr has a single nucleotide mutation in HDS2 that caused Ser1,005Phe alteration. The black triangle represents the insertion site of T-DNA in the SALK_103014 line. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of the flanking region of the fwr mutation of Gea/GNOM/GBF family members. Budding yeast Gea1p and Gea2p (ScGea1p and ScGea2p), Caenorhabditis elegans GBF1 (CeGBF1), human GBF1 (HsGBF1) and Arabidopsis GNL1 and GNL2. Sequences were aligned using ClutstalW. The mutated residue (Ser1,005Phe) in fwr is highlighted in orange. (C) Allelism test between the fwr mutant and the GNOM knockout T-DNA mutant (SALK_103014). Scale bars indicate 10 mm (Col) and 2 mm (gnomSALK_103014), respectively. (D) Accumulation of GNOM mRNA in Col and fwr mutant seedling roots. The black lines in (A) indicate the amplified regions by RT–PCR. The expression of the ACT2 gene was used as a control.
