Figure 1.
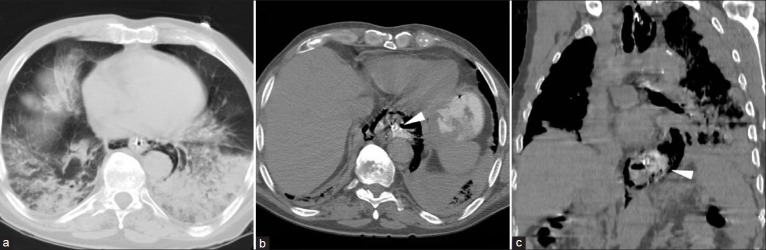
On an axial image from initial CT acquisition (a) viewed at lung window settings) an abnormal air collection is detected in the posterior mediastinum, surrounding the collapsed distal esophagus with nasogastric tube. Basal lung infiltrates, with extensive involvement of the left inferior lobe, are consistent with aspiration pneumonia. Further investigation with CT esophagography (axial image in (b) coronal reformation in (c) visualize increasing posterior pneumomediastinum and extraluminal water-soluble contrast leakage (arrowheads) indicating full-thickness esophageal perforation
