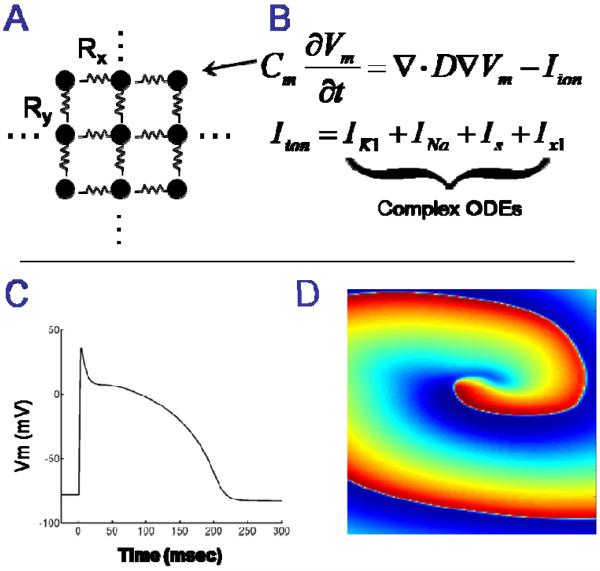
Figure 1.
A: Cardiac muscle is modeled as a large geometrical network of nodes that are electronically coupled. B: The electrical potential of the cell membrane at each node is represented as a large set of differential equations. C: Numerical integration of the differential equations provides transmembrane voltage (action potentials) at each node. D: Spatiotemporal visualization of transmembrane voltage reveals electrophysiological mechanisms of arrhythmias (an electrical rotor is shown).