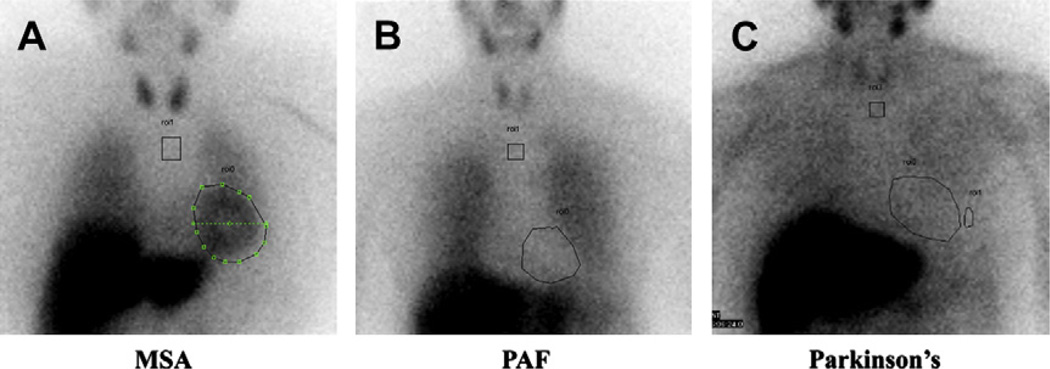
Fig. 3.
Cardiac sympathetic nerve integrity. Cardiac sympathetic nerve integrity can be assessed with m-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scans with a chest view at 4 hours postinjection. MIBG is taken up by intact presynaptic norepinephrine transporters on postganglionic sympathetic neurons, and is not present in the setting of significant postganglionic sympathetic neuropathy. In MSA (A), the lesions are central and preganglionic. Because there is not postganglionic involvement, the heart takes up MIBG avidly. In contrast, patients with pure autonomic failure (PAF) (B) have a significant postganglionic sympathetic neuropathy, and the heart cannot be seen because it cannot take up MIBG. (C) Scan of a patient with Parkinson disease. Although the motor features of Parkinson disease are caused by central nervous system lesions, the autonomic failure is caused by a peripheral postganglionic sympathetic neuropathy, with poor cardiac uptake of MIBG.