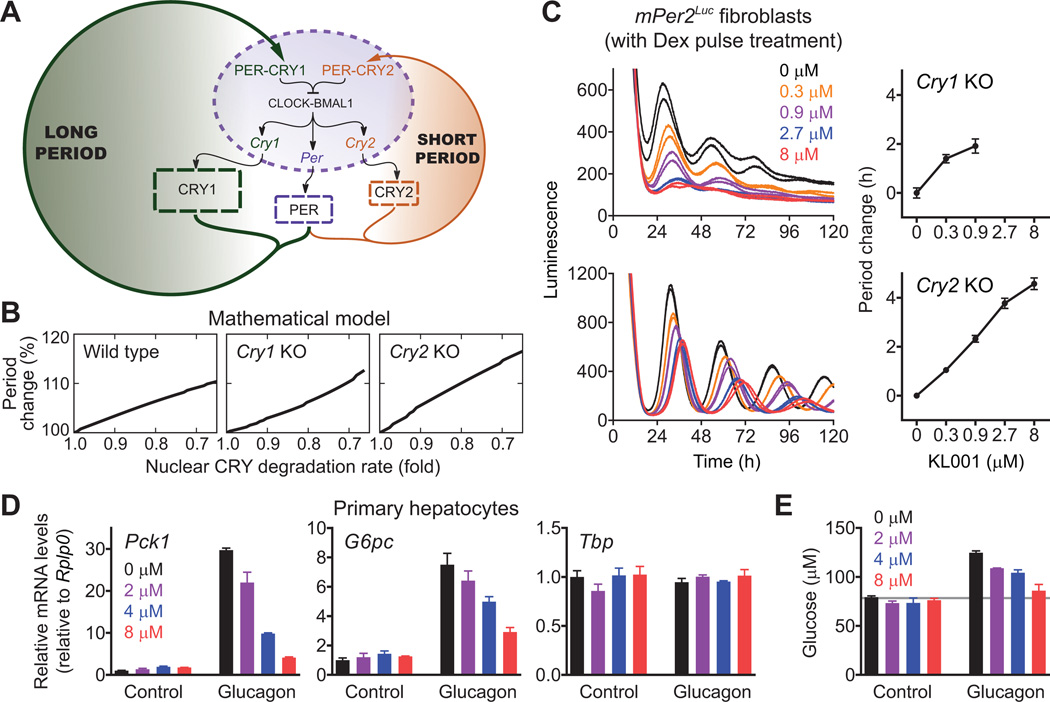
Fig. 4.
Application of KL001 to define roles of CRY isoforms (A to C) and to control hepatic gluconeogenesis (D and E). (A) Scheme of the mathematical model consisting of the two parallel CRY feedback loops. (B) Effect of nuclear CRY stabilization on the period in wild type, Cry1 knockout and Cry2 knockout cells in silico. (C) Cry1 or Cry2 knockout mPer2Luc knock-in mouse fibroblasts were stimulated with dexamethasone (Dex) for 2 h, and luminescence rhythms were monitored in the presence of KL001. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 4). (D and E) Mouse primary hepatocytes were treated with KL001 for 18 h and then stimulated with 10 nM glucagon for 2 h (D, for RT-qPCR analysis) or 3 h (E, for glucose assay). To measure glucose production, the cells were further incubated with glucose-free buffer containing 20 mM sodium lactate and 2 mM sodium pyruvate for 4 h (E). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3).