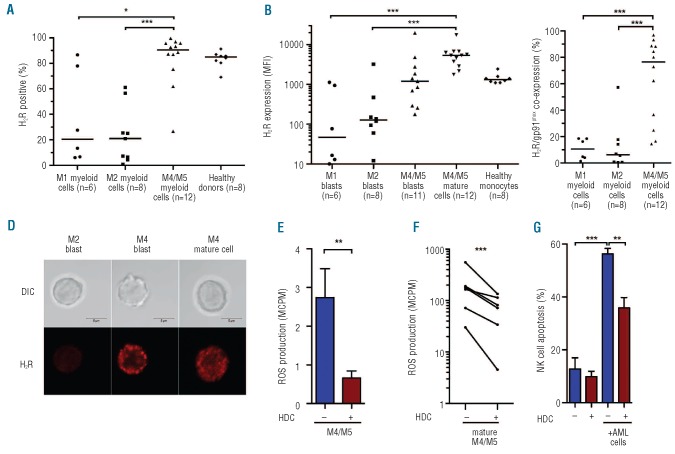
Figure 2.
Distribution and function of H2Rs on morphological subtypes of AML. H2R expression was analyzed by FACS on PBMC or bone marrow from newly diagnosed AML patients (n=26). (A) Percentage of myeloid cells (defined as CD33+ and/or CD34+) expressing H2Rs in cells from patients with AML of indicated FAB classes. (B) Median fluorescence intensity of H2R expression on immature blasts (CD33+ and/or CD34+, CD14- and CD15- myeloid cells) or mature CD14+ leukemic cells. Horizontal lines represent median values. (C) Fraction of CD33+ and/or CD34+ myeloid cells co-expressing H2R and gp91phox in patients with different morphological subtypes of AML. (D) H2R expression visualized by confocal microscopy on immature FAB-M2 cells, immature FAB-M4 cells, and mature FAB-M4 leukemic cells. Bars represent 5 μm. (E) Bars show extracellular ROS production, assayed in the presence or absence of histamine (100 microM) in bone marrow cells from patients with FAB-M4/M5 AML, evaluated using one-sample t-test. (F) Extracellular ROS production by FACS-sorted mature (CD14+) FAB-M4/M5 cells and its inhibition by histamine (P<0.001, one sample t-test). (G) NK cell apoptosis after overnight culture of NK cells from healthy donors with mature CD33+CD14+ FAB-M4/M5 AML cells. Data are from the first NK:AML cell ratio to reach 40% apoptosis (range 8:1 to 2:1; n=5). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.