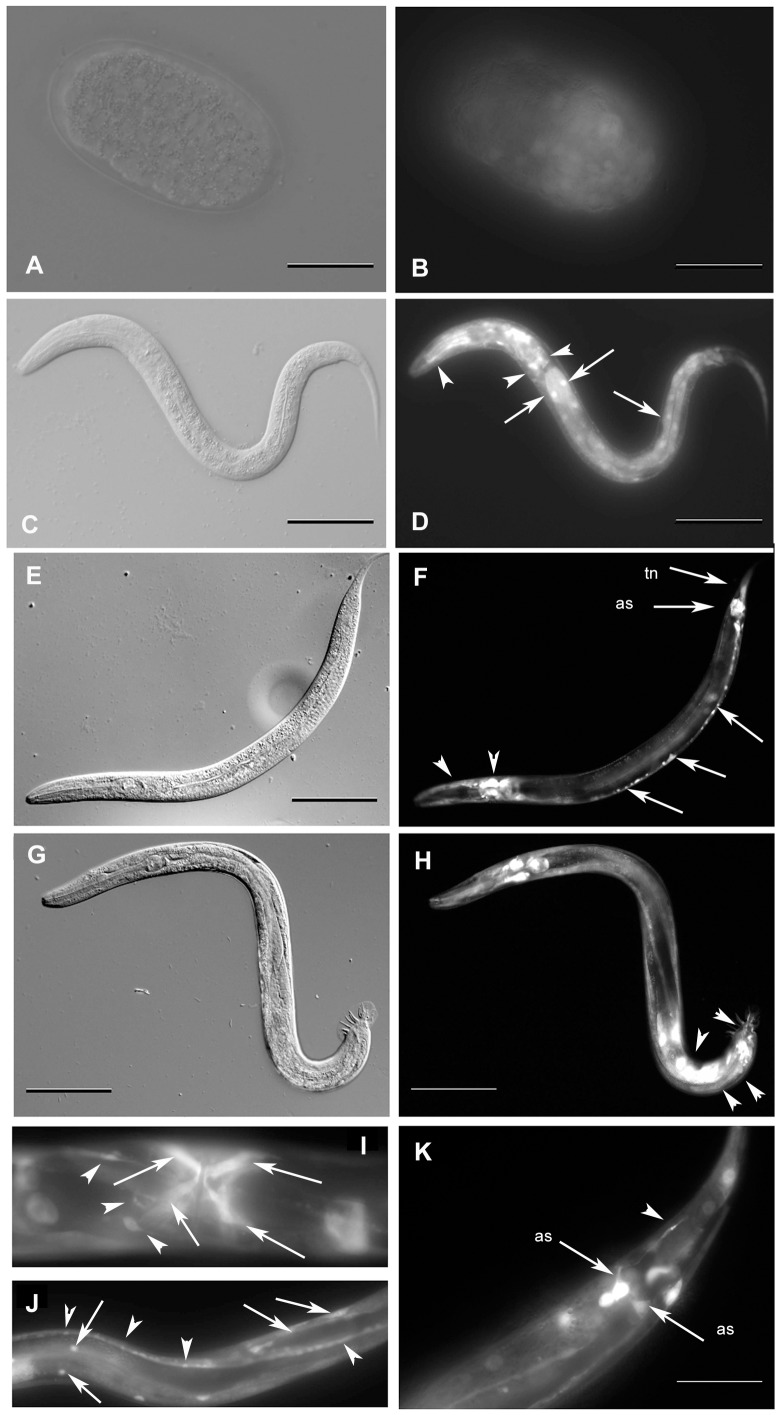
Figure 4. Analysis of gei-8 expression using transgenic lines.
The expression of gei-8 was studied using transgenic lines carrying three different predicted promoters (#1, #2 and #3) fused with gene coding for GFP (indicated in Figure 2C) gei-8::GFP. Panels B and D show the expression from promoter #1 and panels F, H, I, J and K show the expression from promoter #3. Expression from promoter #2 construct was identical with that from promoter #3 and is not shown. (A and B) Embryonic GFP expression is ubiquitously present since comma stage. (C and D) L2 larva expressing gei-8::GFP ubiquitously with the highest expression in the head neurons and in the neuronal ring (arrowheads) and intestinal cells (arrows). (E and F) Expression of GEI-8::GFP in pharyngeal neurons (arrowheads), ventral nerve cord (arrows), anal sphincter (arrow - as) and tail neurons (arrow - tn) of an L4 larva. (G and H) Expression of GEI-8::GFP in L4 male larva. Additional expression is seen in male specific neurons (arrowheads). (I) L4 larva expressing GEI-8::GFP in egg laying structures, vulval and uterine muscles (arrows), egg laying neurons (arrowheads). (J) GEI-8::GFP expression in somatic muscles (arrows) and nerve cord (arrowheads). (K) Detail of expression of GEI-8::GFP in hermaphrodite tail neuron (arrowhead) and anal sphincter (arrows - as). (Figs. A, C, E, G in Nomarski optics and B, D, F, H, I, J, K in fluorescence microscopy). Scale: A, B, I, J 20 µm; C, D, E, F, G, H 100 µm; K 50 µm.