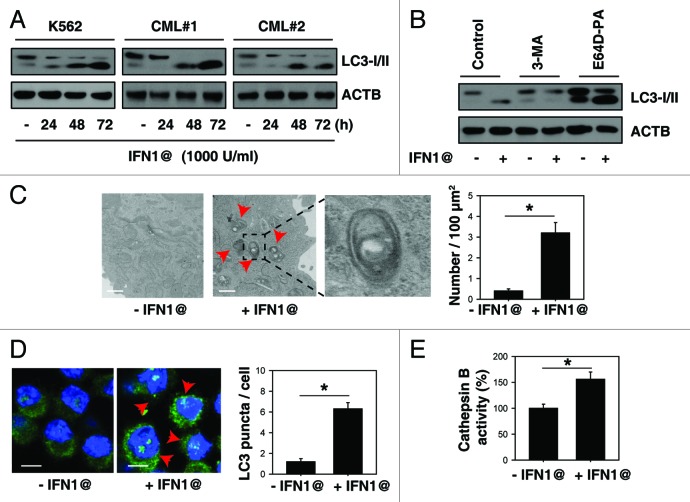
Figure 1. IFN1@ induces autophagic flux in CML cells. (A) K562 cells and primary BMMCs from CML patients were treated with IFN1@ (1000 U/ml) for 24–72 h and the LC3 level was assayed by western blot (n = 3, *p < 0.05). AU, arbitrary units. (B) Analysis of LC3 processing by autophagy in the presence or absence of lysosomal protease inhibitors pepstatin A (PA, 10 μg/ml) and E64D (10 μg/ml) or 3-methyladenine (3-MA, 10 mM) after IFN1@ (1000 U/ml) treatment for 48 h (n = 3, *p < 0.05). AU, arbitrary units. (C) Ultrastructural features in K562 cells with or without IFN1@ (1000 U/ml, 48 h) treatment. By definition, autophagic vacuoles are limited by a double, or occasionally multilayered membrane.16 They contain cytoplasmic material or organelles. Sometimes the autophagic vacuole membrane does not have any contrast in thin sections. This is probably caused by extraction of lipids during sample preparation, as lipids are not optimally preserved in conventional aldehyde fixation.16 The inset in (C) shows a magnified double-membrane autophagic vacuole. The number of autophagic vacuoles (indicated by the red arrows) under TEM was calculated (*p < 0.05). (D and E) K562 cells were treated with IFN1@ (1000 U/ml) for 48 h and LC3 puncta per cell and enzymatic activity of cathepsin B were assayed by confocal microscopy (D) and ELISA (E) as described in the methods section (*p < 0.05). Representative images in K562 cells are shown in the left panel (D). Scale bar, 10 μm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.