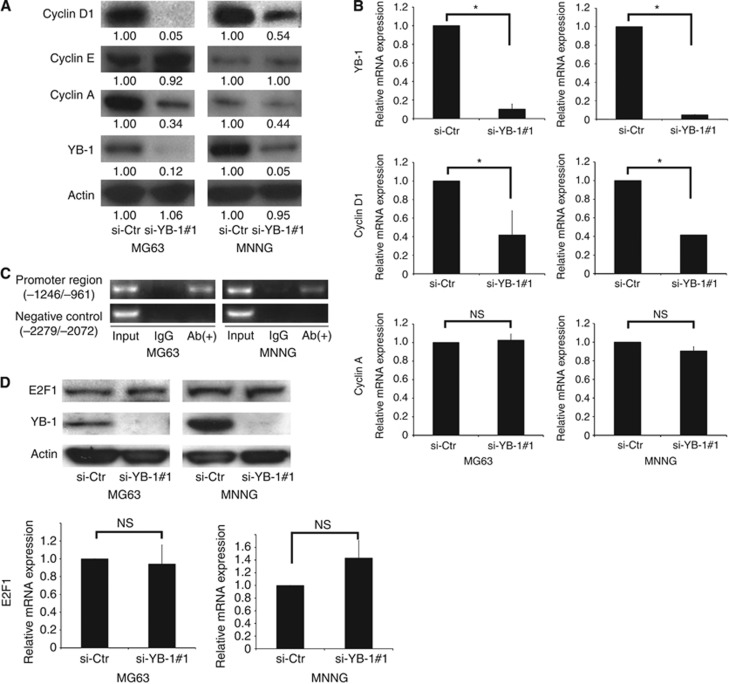
Figure 3.
Silencing the YB-1 gene in OS cells modulates cell cycle-related genes. (A) Effect of YB-1 knockdown on expression of cyclin D1, cyclin E, cyclin A, YB-1, and actin protein was analysed by immunoblotting. Cells were incubated with 50 nmol l−1 of si-Ctr or si-YB-1#1 for 48 h, and lysates were prepared. (B) Effect of YB-1 knockdown on cyclin D1 and cyclin A mRNA expression. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data are expressed as the mean±s.d. *P<0.05. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation of cyclin D1 gene promoters using YB-1 antibody. Chromatin from MG63 and MNNG cell lines were cross-linked to fix bound proteins to the DNA. Cells were lysed and the chromatin was incubated with a YB-1 antibody to immunoprecipitate promoters bound by YB-1. Polymerase chain reaction was then performed to amplify promoter fragments to known to YB-1 bound. Input=DNA before immunoprecipitation; IgG=ChIP with the IgG-negative control antibody; Ab=YB-1 antibody. Figure shows typical results obtained from at least three independent experiments. (D) Effect of silencing of the YB-1 gene on expression of E2F1, and YB-1 protein was analysed by immunoblotting. Actin was used for internal normalisation. Effect of YB-1 knockdown on E2F1 mRNA expression. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data are expressed as the mean±s.d. NS=nonsignificant.