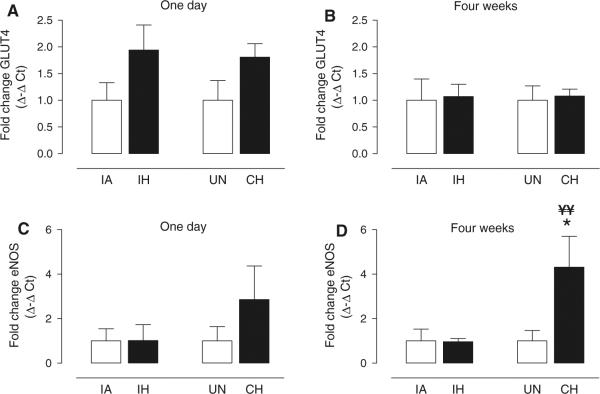
Fig. 7.
Biochemical and molecular responses to 1-day and 4-week exposure to IH or CH in skeletal muscle. Mean ± SE values for fold change (Δ–Δ cycle threshold; CT) in expression of a glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) and b endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) for intermittent hypoxia (IH) and continuous hypoxia (CH) groups relative to respective intermittent air (IA) and unhandled (UN) control groups after 1 day or 4 weeks of exposure. Significance determined by one-way ANOVA with differences between the means of the four experimental groups at 1 day or 4 weeks assessed by a post-hoc Newman–Keuls test. Statistical differences were determined from Δ CT between GLUT4 or eNOS and 18S ribosomal RNA. *p < 0.05 CH versus UN; ¥¥p < 0.025 CH versus IH; n = 6–9 per group