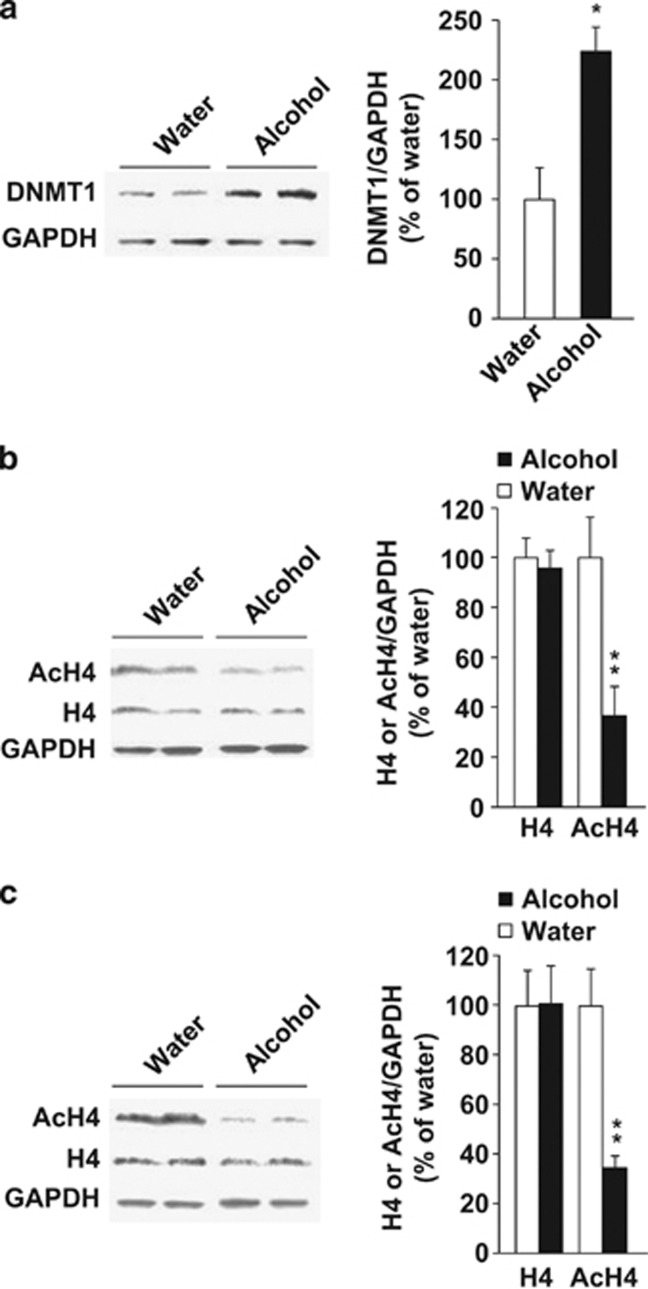
Figure 5.
Excessive alcohol intake increases DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) levels and reduces the level of Histone H4 acetylation. (a) Mice nucleus accumbens (NAc) slices were collected 4 h after the beginning of 20% alcohol access. DNMT1 level was determined by western blot analysis. Age-matched alcohol-naïve mice consuming only water were used as control. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Results are expressed as mean of image density of DNMT1/GAPDH±s.e.m., *P<0.05 compared with water. n=3. (b) Mice NAc slices were collected after a 4-h session of 20% alcohol access in the drinking in the dark (DID) procedure. Age-matched alcohol-naïve mice consuming only water were used as control. Total histone H4 (H4) and acetylated H4 (AcH4, pan-acetylated-lysine antibody) levels were determined by western blot analysis. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Results are expressed as mean of image density of H4 or AcH4/GAPDH±s.e.m., **P<0.01 compared with water. n=6–7. (c) Rat NAc slices were collected at the end of a 20% alcohol operant self-administration session of 30 min. The controls, age-matched alcohol-naïve rats, were concomitantly confined to the behavioral chamber for 30 min with access to the levers, but lever presses had no associated consequences. Results are expressed as mean H4 or AcH4/GAPDH±s.e.m., **P<0.01 compared with water. n=4–5.