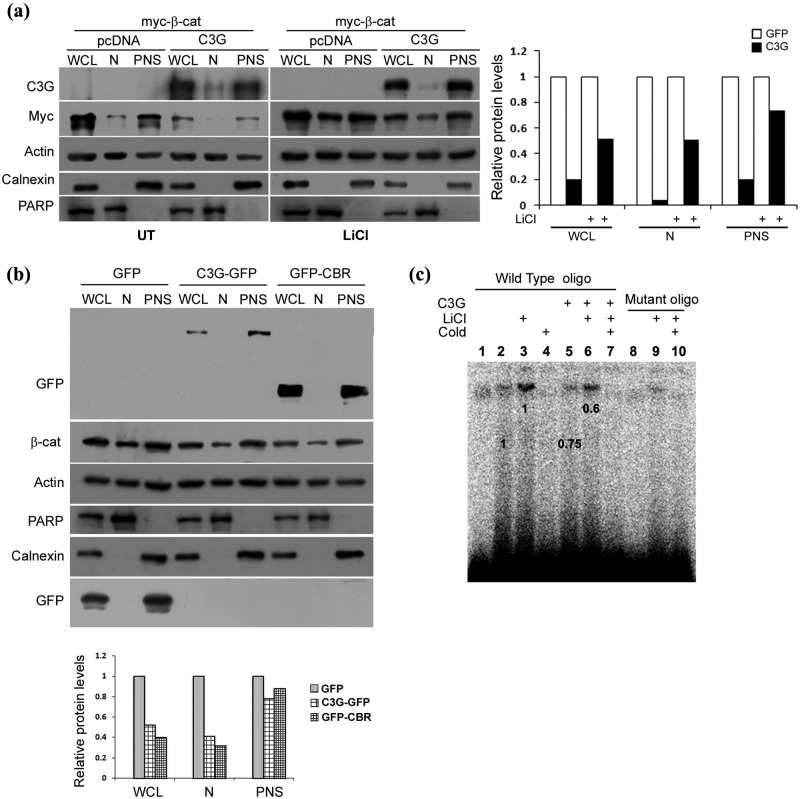
Figure 4.
C3G reduces nuclear levels of β-catenin. (a) Effect of C3G expression on exogenously expressed β-catenin in nuclear and postnuclear fractions (PNS). C3G was co-expressed with myc β-catenin in HEK 293T cells and β-catenin protein analyzed in whole cell lysate (WCL), nuclear (N), and postnuclear fractions (PNS) in untreated or LiCl treated cells. Actin was used as loading control. Calnexin and PARP are used as markers for establishing purity of postnuclear and nuclear fractions, respectively. Relative change in β-catenin in subcellular fractions upon C3G expression is shown in bar diagram. (b) Effect of C3G and CBR expression on endogenous nuclear β-catenin levels in cells treated with LiCl. HEK 293T cells expressing GFP, C3G-GFP, or GFP-CBR were treated with LiCl, and cellular β-catenin levels in nuclear and postnuclear fraction were examined by Western blotting. Calnexin and PARP are used to ascertain the purity of PNS and N fractions, respectively. Relative change in β-catenin in subcellular fractions upon C3G-GFP or GFP-CBR expression is shown in bar diagram. (c) Nuclear extracts from C3G expressing cells show reduced binding to TCF binding consensus oligo. EMSA was performed using nuclear extracts of untransfected or C3G transfected HEK 293T cells with or without LiCl treatment and TCF binding consensus (wild-type) or mutant oligo. Specificity of the band is shown by using 100-fold molar ratio excess of unlabeled oligo (cold). Lanes 1 and 10 are devoid of nuclear extracts. Numbers on the figure indicate relative change in band intensity upon C3G expression.