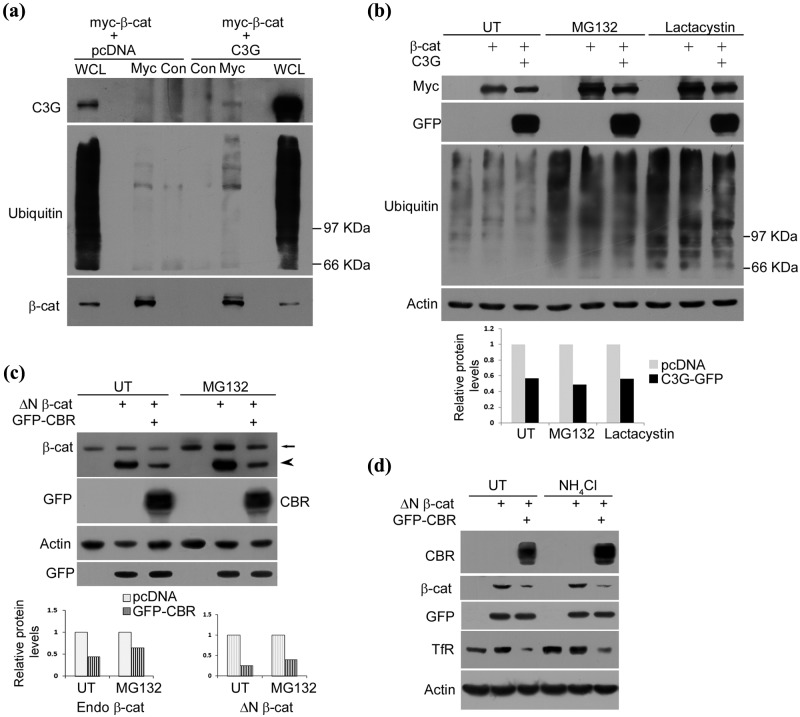
Figure 5.
C3G causes repression of β-catenin levels under conditions of proteasomal inhibition. (a) C3G co-expression enhances ubiquitination of β-catenin. HEK 293T cells transfected with myc tagged β-catenin along with pcDNA or C3G expression constructs were treated with MG132 and subject to immunoprecipitation using myc antibody or normal mouse IgG (Con) followed by Western blotting to detect the indicated proteins with antibodies. (b) C3G represses co-expressed β-catenin protein independent of proteasomal degradation. HEK 293T cells were transfected with 200 ng of β-catenin and 200 ng of pcDNA or C3G expression constructs and were either left untreated (UT) or treated with MG132 or lactacystin for 8 hours after 22 hours of expression. Cell lysates were subject to Western blotting to detect the indicated proteins. Actin was used as loading control. Bar diagram shows relative change in β-catenin levels due to C3G expression. (c) HEK 293T cells were transfected with 200 ng of ΔN β-catenin and 200 ng of pcDNA or CBR-GFP along with 20 ng of GFP expression constructs and treated as in (b). Cell lysates were subject to Western blotting to detect the indicated proteins. Arrow and arrowhead indicate endogenous β-catenin and overexpressed ΔN β-catenin, respectively. GFP was used as transfection control and actin as loading control. Bar diagram shows densitometric analysis of relative change in endogenous β-catenin and ΔN β-catenin levels due to GFP-CBR expression. (d) CBR induced β-catenin repression is independent of lysosomal degradation. HEK 293T cells were transfected as in (c) and treated with 20 mM NH4Cl after 6 hours of expression. Cell lysates made after 30 hours of expression were subject to Western blotting to detect the indicated proteins with antibodies. Cellular TfR was examined to show effect of NH4Cl treatment.