Figure 1.
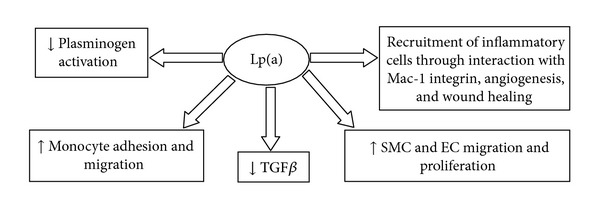
Mechanisms underlying the Lp(a)-induced cardiovascular disease. Lp(a) inhibits the activation of TGF and promotes the proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells to endothelial cells. Moreover Lp(a) inhibits plasminogen activation and decreases the activity of fibrin-dependent tissue-type plasminogen activator.
