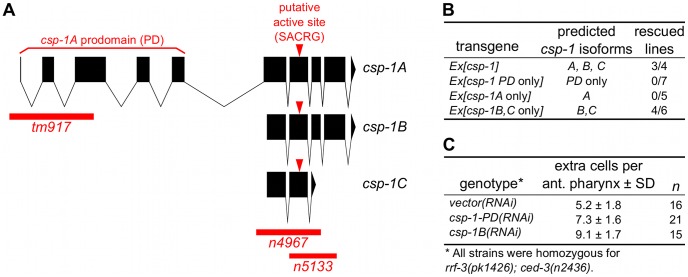
Figure 1. The B and/or C isoforms of csp-1 promote programmed cell death.
(A) Representations of the intron-exon organization of the three known csp-1 mRNA isoforms (A, B and C). Red bars indicate the csp-1 deletion alleles used in this study; arrowheads indicate the SACRG sequence that encodes the caspase active-site. The graphic was generated using the Intron-Exon Graphic Maker (N. Bhatla; www.wormweb.org). (B) Extrachromosomal arrays carrying a wild-type genomic fragment of the csp-1 locus or a mutant version that expresses only the B or C isoforms can rescue the csp-1(n4967) mutant phenotype. The csp-1 PD-only transgene contains two nonsense mutations that encode early stop codons affecting the B and C mRNA isoforms; the csp-1A-only transgene contains a mutation that changes the B/C start codon to an alanine codon; and the csp-1B/C-only transgene contains two nonsense mutations that encode early stop codons affecting the A isoform. The csp-1 transgenes were injected into csp-1(n4967); ced-3(n2436) animals, and the resulting independent lines were assayed for csp-1 rescuing activity by counting the number of extra undead cells in the anterior pharynx. The transgenes and their constructions are described in detail in Materials and Methods, and the complete data for each transgenic line are provided in Table S2. (C) RNAi knockdown of csp-1 phenocopies the csp-1 mutations. dsRNAs targeting the csp-1 pro-domain or the csp-1B isoform were in vitro transcribed and injected into the gonads of RNAi-sensitive rrf-3(pk1426); ced-3(n2436) adult hermaphrodites. Progeny of the injected adults were assayed for extra undead cells in the anterior pharynx. PD, prodomain.