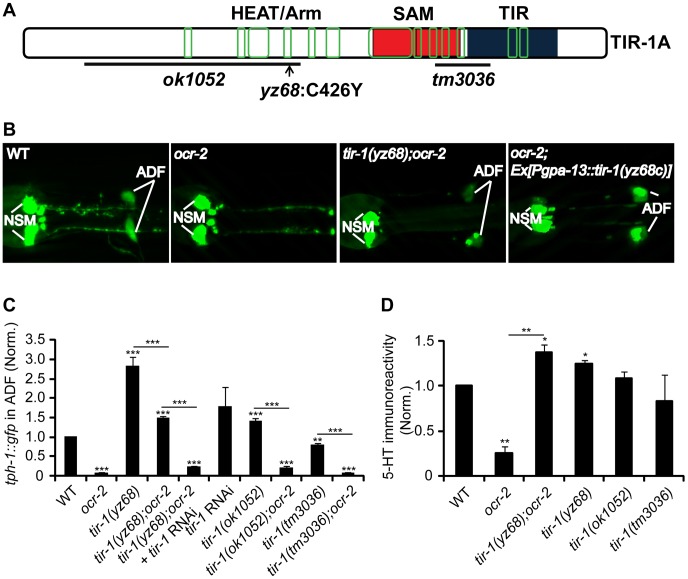
Figure 1. tir-1(yz68gf) mutants constitutively upregulate tph-1::gfp expression in ADF neurons.
A. Mutations in predicted tir-1 protein. The TIR-1 structure is adapted from a previous report [8]. Blue, red and green denote the TIR domain, SAM domains, and regions containing the HEAT/Arm motifs, respectively. B. Photomicrographs showing that tir-1(yz68gf) mutation and transgenic expression of tir-1(yz68gf) cDNA enhanced ADF tph-1::gfp expression. ocr-2 background was used to reduce basal ADF tph-1::gfp for a better detection of tph-1::gfp upregulation by tir-1(yz68gf). C. Quantification of ADF tph-1::gfp fluorescence in tir-1(lf) and tir-1(gf) mutants under optimal growth conditions. tir-1(yz68gf) mutants displayed enhanced ADF fluorescence on its own and in ocr-2 backgrounds relative to corresponding controls, and RNAi of tir-1 abolished tph-1::gfp upregulation by tir-1(yz68gf). The value of GFP fluorescence in the ADF neurons of mutants is normalized to that of WT animals. For RNAi experiments, the value of tir-1 RNAi is normalized to that in the same strain but treated with an empty vector. Each bar represents the average of at least three trials ± SEM. Throughout of this paper, statistics between WT and individual mutants is marked on the top of each bar, and that between two mutant strains or two treatments is indicated on the top of the line across compared strains, *** p<0.001. D. Quantification of 5-HT immunoreactivity in ADF neurons of tir-1 mutants. Data represent the average of two trials, each with at least 20 L4-stage animals per strain ± SEM, and the value of the mutants is normalized to that of WT animals stained in parallel, *p<0.05, ** p<0.01.