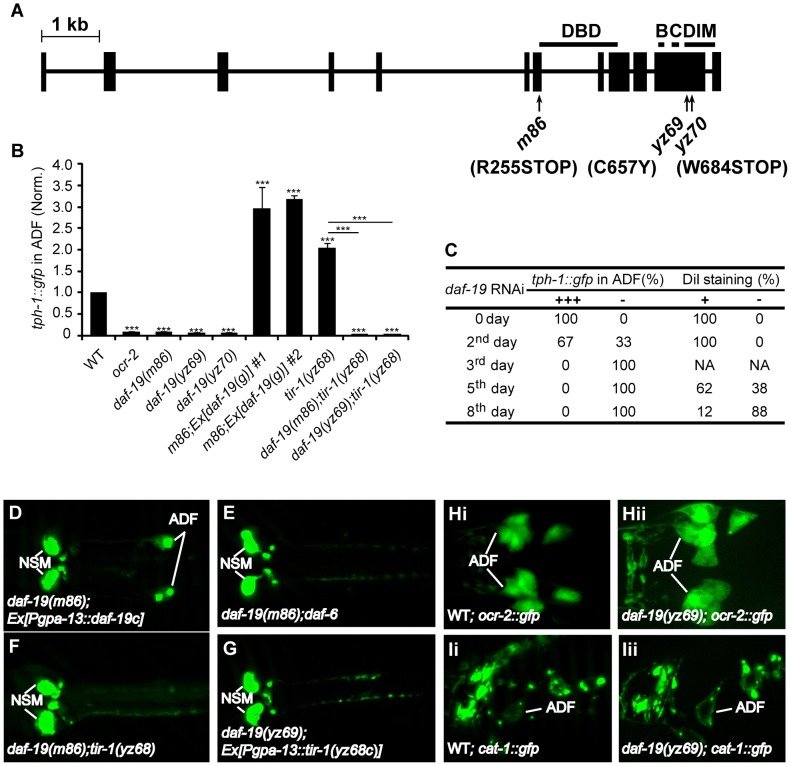
Figure 3. daf-19 is required for tph-1 expression in the ADF neurons.
A. Mutations in the daf-19 gene. The daf-19 gene structure is adapted from a previous report [17]. Boxes denote exons and the line denotes introns. The areas containing the DNA binding domain (DBD), dimerization domain (DIM) and conserved B and C regions are indicated. B. ADF tph-1::gfp is dramatically reduced in daf-19 mutants and daf-19;tir-1(yz68gf) double mutants. Two transgenic lines expressing WT daf-19 genomic sequence rescued tph-1::gfp expression in daf-19(m86)-null mutants. *** p<0.001. C. RNAi of daf-19 after embryogenesis. L1 larvae with normal ADF tph-1::gfp and cilial morphology were fed E. coli expressing RNAi clone against daf-19. tph-1::gfp was quantified on indicated days, and dye filling of chemosensory neurons with fluorescence dye DiI was performed to monitor gross cilia morphology of the chemosensory neurons. daf-19 RNAi eliminated ADF tph-1::gfp (-) and eliminated dye filling of the cilia, but tph-1::gfp was abolished in many animals prior to a detectable change in the cilia morphology. -, No discernible fluorescence of tph-1::gfp or DiI staining in the neurons. D–G. Photomicrographs showing tph-1::gfp in daf-19 mutants under various genetic backgrounds. daf-19 deficiency abolished tph-1::gfp expression in the ADF neurons of both daf-6 and tir-1(yz68gf) backgrounds. H–I. Expressions of ADF marker genes in daf-19 mutants. ocr-2::gfp and VMAT cat-1::gfp were comparable between WT (Hi and Ii) and daf-19 mutant (Hii and Iii) animals, suggesting that daf-19 deficiency does not grossly alter ADF cell fates.