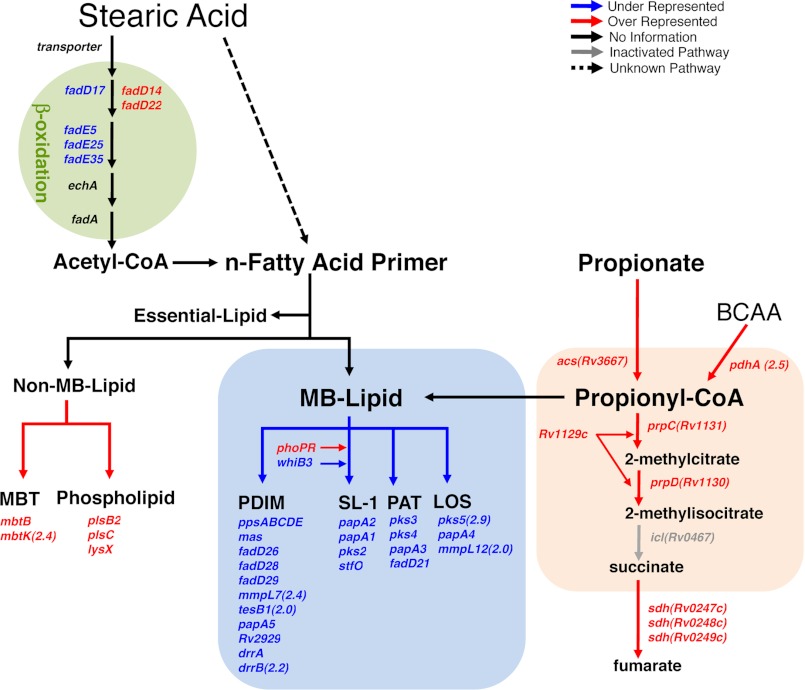
FIGURE 6.
Phenotypic TraSH screen identifies genes involved in propionate utilization and toxicification. Graphic illustration of the differentially represented genes in the context of the metabolic pathways most relevant to propionate utilization and detoxification. Genes required for Δicl1 Mtb growth in the presence propionate and long chain fatty acids as a means of propionate toxicity rescue are indicated in blue type. Genes that, when mutated, enhance Δicl1 Mtb growth in the presence of propionate and long chain fatty acids are indicated in red type. The differentially represented genes are shown in relation to the relevant carbon metabolic pathways: synthesis of non-essential MB lipids, synthesis of non-MB lipids, the MMC, and genes involved in the β-oxidation breakdown of long chain fatty acids. All genes selected were >3-fold overrepresented or >3-fold underrepresented with p < 0.05. The full list of overrepresented and underrepresented genes is provided in supplemental Tables S1 and S2. BCAA, branched chain amino acids; PAT, polyacyltrehalose; LOS, lipooligosaccharide.