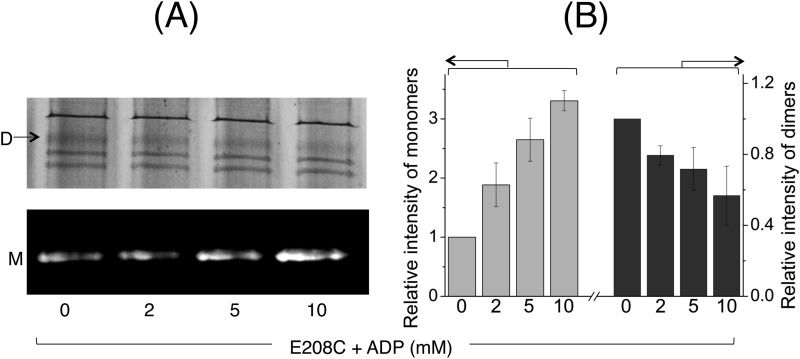
FIGURE 9.
ADP-responsive cross-linking Atto590 labeling of E208C MsbA-cl. A, to study the conformational changes affected by ADP binding, E208C MsbA-cl harboring ISOVs were assayed using cysteine cross-linking Atto590 labeling in the presence of increasing concentrations of ADP. Briefly, ISOVs at 5–7 mg/ml total membrane protein, in 100 mm K-HEPES buffer, pH 7.0, containing 5 mm MgSO4 were first mixed with 0.5 mm DTT for 3 min at room temperature to reduce preformed cross-links. ADP was added at the indicated concentrations. Following 3 min of incubation at RT, cross-linking was initiated by the addition of 0.5 mm copper phenanthroline. After 5 min of incubation in a 30 °C shaker incubator, 20 μm Atto590 was added, and the samples were further incubated for 10 min in the 30 °C shaker incubator. Reactions were stopped by the addition of 10 mm N-ethylmaleimide. 10–15 μg of protein from each sample was mixed with 6× SDS sample loading buffer devoid of reducing agents and separated on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The gel was first viewed under UV light to detect Atto-labeled monomers (M; bottom panel), followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining to detect dimers (D; top panel). B, monomer/dimer intensities are presented as percentage of total intensity of MsbA-related bands (monomers + dimers), relative to the percentage monomer/dimer intensity observed under the no nucleotide condition (which was set at as 1) (n = 3, data are mean ± S.E.). The results suggest that ADP binding to MsbA induces a conformational shift toward the inward-facing state.