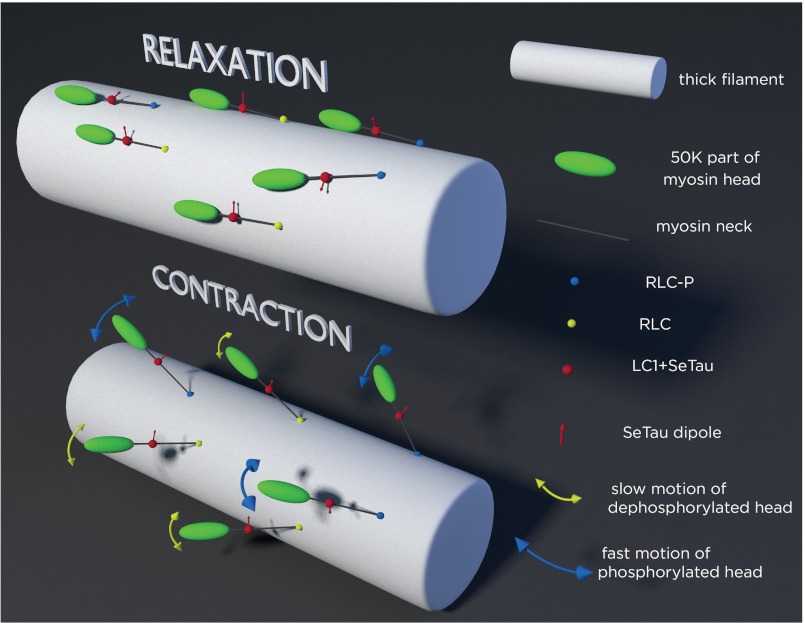
FIGURE 10.
Schematics of the arrangement of cross-bridges on the surface of thick filament (white cylinder). Phosphorylated and dephosphorylated RLC are indicated by blue and yellow spheres, respectively. Red sphere is the LC1 containing rhodamine; its transition dipole is indicated by red arrows. Top panel, relaxation, dephosphorylated myosins are well oriented, the transition dipoles point approximately in the same direction. Dephosphorylated myosins are in the SRX state. In contrast, phosphorylated myosins are not well oriented. Both phosphorylated and dephosphorylated myosins are largely immobilized by thick filament core. Bottom panel, contraction, now cross-bridges leave the surface of thick filaments to be able to interact with thin filaments (not shown). Both types of myosins are equally disorganized and rotate slow during relaxation, but phosphorylated myosins are more mobile during contraction. Blue and yellow arrows imply rotation. Rotation occurs in both the polar and azimuthal planes. Thickness of the yellow and blue arrowheads indicates the speed of rotation. Dephosphorylated heads (yellow arrows) move slower than phosphorylated heads (blue arrows).