FIGURE 6.
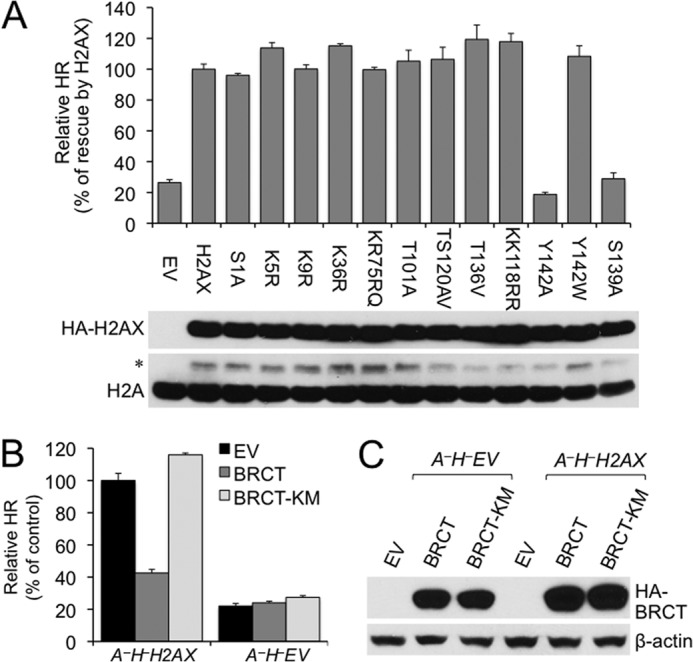
Disruption of the γ-H2AX/MDC1 interaction abolishes H2AX-dependent HR in ATM−/− ES cells. A, effect of H2AX mutations on H2AX-dependent HR in ATM−/− cells. A−H− ES cells were transiently transfected with expression plasmids for WT and mutant H2AX as indicated. Relative HR of A−H− cells transfected with WT H2AX serves as control. Bars represent the mean of triplicates. Error bars indicate S.E. Statistical significance was determined by paired t test between H2AX and other samples: not significant (p > 0.05) except that p < 0.004 between H2AX and EV, Y142A, or S139A and p < 0.002 between Y142A and Y142W. H2AX protein levels after transient transfection of H2AX alleles are shown under the chart. Exogenous HA-tagged WT and mutant H2AX recognized by anti-HA antibody are indicated with histone H2A as the loading control. * indicates exogenous HA-tagged H2AX recognized by anti-H2A antibody. B, effect of MDC1 BRCT on H2AX-dependent HR in ATM−/− cells. I-SceI-induced HR assays were performed on A−H−H2AX and A−H−EV ES reporter cells transiently transfected with EV and expression plasmids for HA-tagged mouse MDC1 BRCT or MDC1 BRCT K1554M (KM). Relative HR of A−H−H2AX cells transfected with EV serves as control. Bars represent the mean of triplicates. Error bars indicate S.E. Statistical significance was determined by paired t test between “BRCT” and others: p < 0.002 in A−H−H2AX and not significant (p > 0.05) in A−H−EV. C, protein levels of MDC1 BRCT and BRCT K1554M produced in I-SceI-induced HR assays and detected by anti-HA antibody. β-Actin serves as a loading control.
