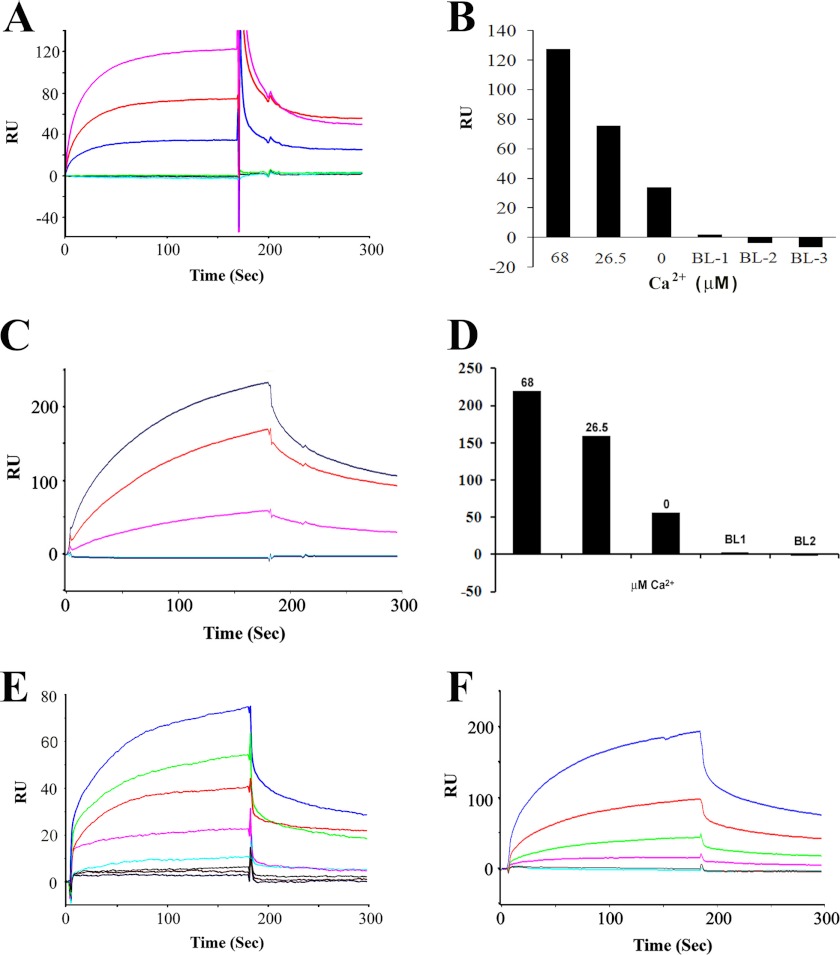
FIGURE 5.
SPR analysis of interactions of CNGA3 with myosin VIIa. A, a SPR sensorgram shows Ca2+-dependent interaction between CNGA3-N (ligand) and myosin VIIa (100 nm, analyte) with maximum response of 130 RU at 68 μm Ca2+ (magenta) compared with 26.5 μm Ca2+ (red). A less but finite amount of binding was observed with 1 mm EGTA (blue). Negative controls included HBS-N + 1 mm EGTA (green), 10 μg/ml bovine serum albumin (gray), and HBS-N buffer alone (cyan). B, shown is a bar graph representation of results for A and in descending order. C, a SPR sensorgram shows a Ca2+-dependent interaction between myosin VIIa (ligand) and CNGA3-N (125 nm, analyte) with maximum response of 217 at 68 μm Ca2+ (blue) compared with that for 26.5 μm Ca2+ (red). Again, there was a smaller but finite response for 1 mm EGTA (magenta). Negative controls included HBS-N + 1 mm EGTA (cyan), HBS-N buffer alone (blue), overlapping in the bottom trace. D, shown is a bar graph representation of results for C in descending order. E, shown is quantitation of CNGA3-N (ligand) and myosin VIIa (analyte) interaction by SPR. Purified myosin VIIa was immobilized on a CM5 sensor chip, and CNGA3-N was diluted in a series of concentrations at 68 μm Ca2+: 100 nm (blue), 50 nm (green), 25 nm (red), 12.5 nm (magenta), 6.25 nm (cyan), 3.0 nm (gray), 1.5 nm (brown), and HBS-N buffer (black). Kinetic constants are summarized in Table 1. F, shown is quantitation of myosin VIIa (ligand) and CNGA3-N (analyte) interaction by SPR. Purified myosin VIIa was immobilized on a CM5 sensor chip, and CNGA3-N was diluted in a series of concentrations at 68 μm Ca2+: 320 nm (blue), 160 nm (red), 80 nm (green), 40 nm (magenta), 20 nm (red), 10 nm (cyan).