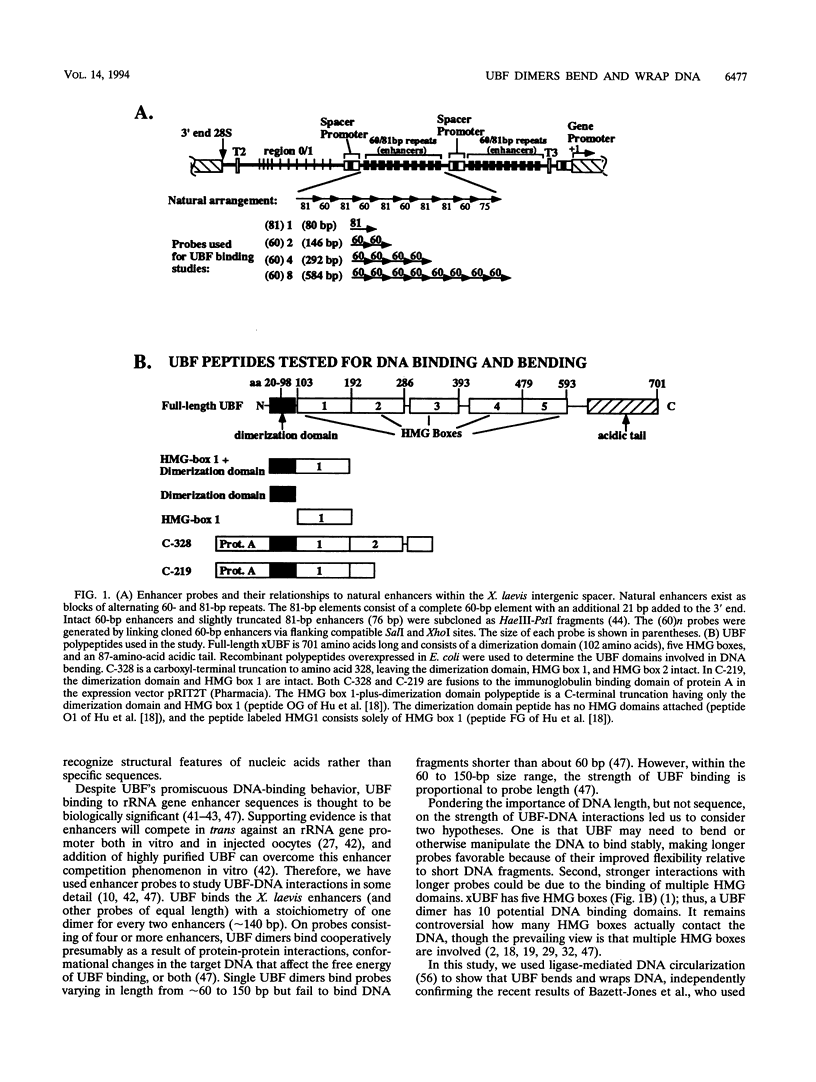
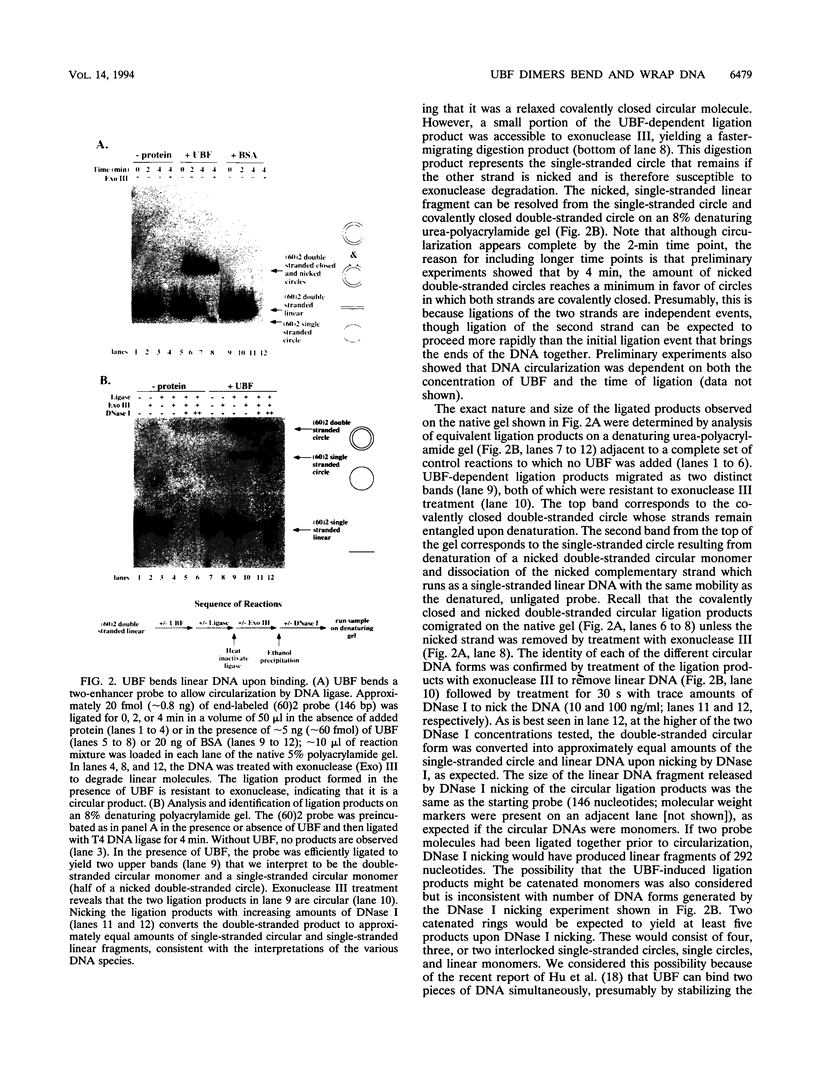
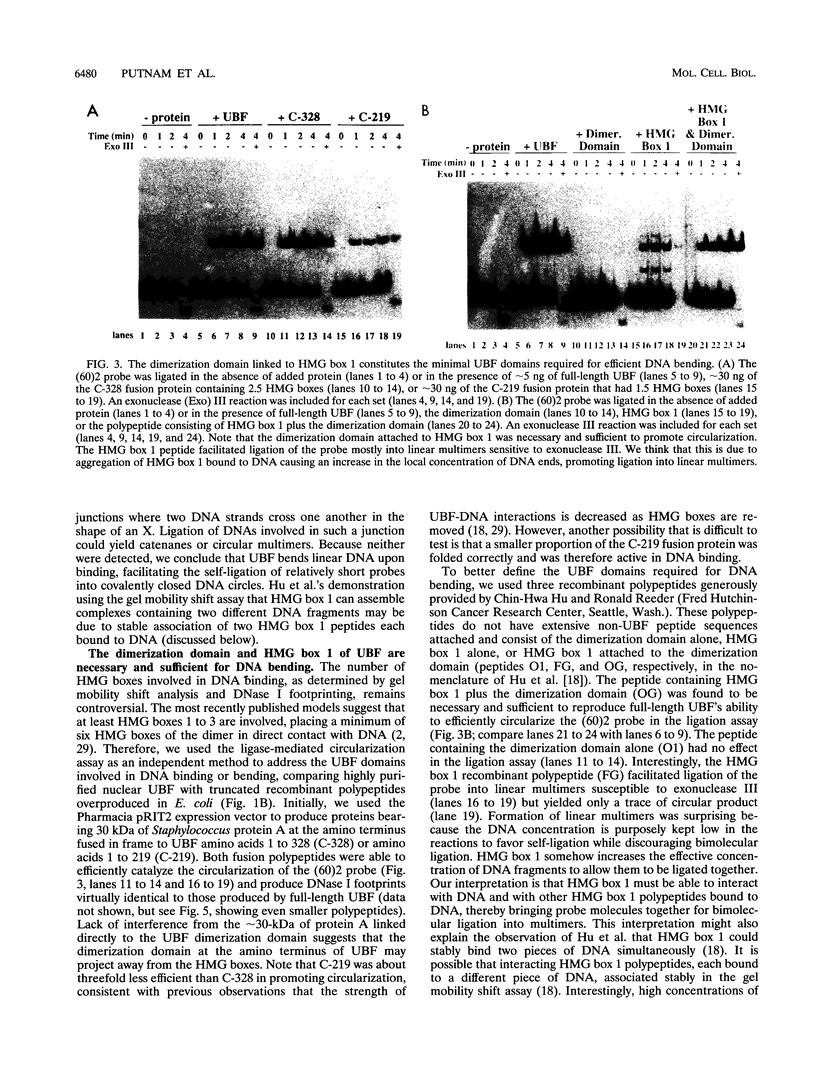
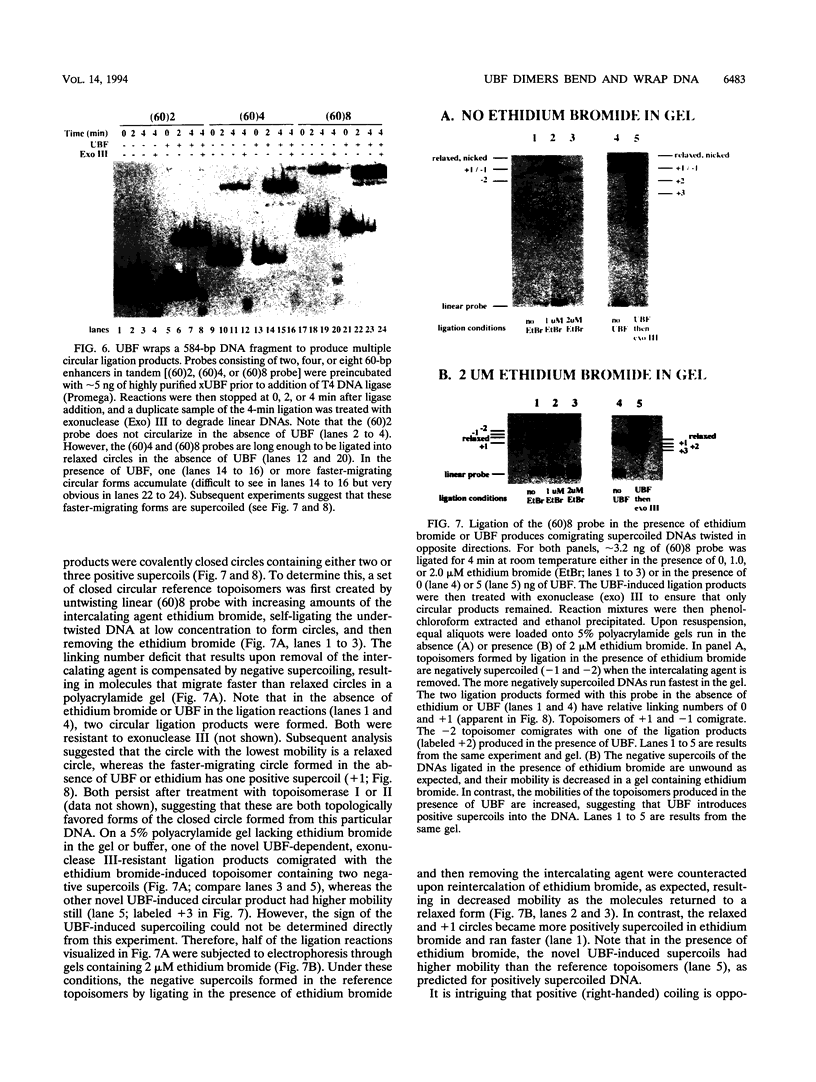
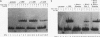Abstract
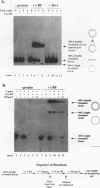
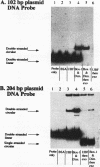
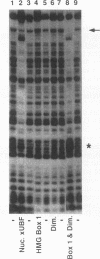
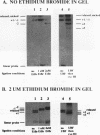
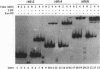
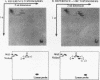
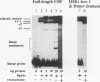
Upstream binding factor (UBF) is an important transactivator of RNA polymerase I and is a member of a family of proteins that contain nucleic acid binding domains named high-mobility-group (HMG) boxes because of their similarity to HMG chromosomal proteins. UBF is a highly sequence-tolerant DNA-binding protein for which no binding consensus sequence has been identified. Therefore, it has been suggested that UBF may recognize preformed structural features of DNA, a hypothesis supported by UBF's ability to bind synthetic DNA cruciforms, four-way junctions, and even tRNA. We show here that full-length UBF can also bend linear DNA to mediate circularization of probes as small as 102 bp in the presence of DNA ligase. Longer probes in the presence of UBF become positively supercoiled when ligated, suggesting that UBF wraps the DNA in a right-handed direction, opposite the direction of DNA wrapping around a nucleosome. The dimerization domain and HMG box 1 are necessary and sufficient to circularize short probes and supercoil longer probes in the presence of DNA ligase. UBF's sequence tolerance coupled with its ability to bend and wrap DNA makes UBF an unusual eukaryotic transcription factor. However, UBF's ability to bend DNA might explain how upstream and downstream rRNA gene promoter domains interact. UBF-induced DNA wrapping could also be a mechanism by which UBF counteracts histone-mediated gene repression.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachvarov D., Moss T. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor xUBF contains 5 tandemly repeated HMG homology boxes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2331–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazett-Jones D. P., Leblanc B., Herfort M., Moss T. Short-range DNA looping by the Xenopus HMG-box transcription factor, xUBF. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1134–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.8178172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–954. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H., Tjian R. Molecular mechanisms governing species-specific transcription of ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Falciola L., Ferrari S., Lilley D. M. The DNA binding site of HMG1 protein is composed of two similar segments (HMG boxes), both of which have counterparts in other eukaryotic regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1055–1063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Buttgereit D., Grummt I. A purified transcription factor (TIF-IB) binds to essential sequences of the mouse rDNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):604–608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conconi A., Widmer R. M., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Two different chromatin structures coexist in ribosomal RNA genes throughout the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90790-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copenhaver G. P., Putnam C. D., Denton M. L., Pikaard C. S. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF is a sequence-tolerant HMG-box protein that can recognize structured nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2651–2657. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M. A transcription factor, TFIS, interacts with both the promoter and enhancer of the Xenopus rRNA genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1768–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M., Dröge P. Transactivation of the Xenopus rRNA gene promoter by its enhancer. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):657–659. doi: 10.1038/341657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Harley V. R., Pontiggia A., Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R., Bianchi M. E. SRY, like HMG1, recognizes sharp angles in DNA. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4497–4506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Lisowsky T., Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. DNA wrapping and bending by a mitochondrial high mobility group-like transcriptional activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3358–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatake K., Nishimura T., Maeda Y., Hanada K., Song C. Z., Muramatsu M. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNA and the gene for mouse transcription factor UBF. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4631–4637. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu C. H., McStay B., Jeong S. W., Reeder R. H. xUBF, an RNA polymerase I transcription factor, binds crossover DNA with low sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):2871–2882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Chow A. M., King D. S., Tjian R. Multiple domains of the RNA polymerase I activator hUBF interact with the TATA-binding protein complex hSL1 to mediate transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1950–1963. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Liu J. F., Wang J. C. Nonhistone proteins HMG1 and HMG2 change the DNA helical structure. Science. 1978 Mar 24;199(4335):1345–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.628842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. Dual role of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: trans-activator and antirepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7340–7344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Stefanovsky V., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription activator UBF relieves Ku antigen-mediated repression of mouse ribosomal gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2057–2063. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Voit R., Stefanovsky V., Evers R., Bianchi M., Grummt I. Functional differences between the two splice variants of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: the second HMG box determines specificity of DNA binding and transcriptional activity. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):416–424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal gene spacer of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc B., Read C., Moss T. Recognition of the Xenopus ribosomal core promoter by the transcription factor xUBF involves multiple HMG box domains and leads to an xUBF interdomain interaction. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):513–525. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Hisatake K., Kondo T., Hanada K., Song C. Z., Nishimura T., Muramatsu M. Mouse rRNA gene transcription factor mUBF requires both HMG-box1 and an acidic tail for nucleolar accumulation: molecular analysis of the nucleolar targeting mechanism. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3695–3704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Frazier M. W., Reeder R. H. xUBF contains a novel dimerization domain essential for RNA polymerase I transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1957–1968. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Hu C. H., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H. xUBF and Rib 1 are both required for formation of a stable polymerase I promoter complex in X. laevis. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Rothblum L. I. Identification of two forms of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Smith S. D., Xie W., Rothblum L. I. Analysis of the phosphorylation, DNA-binding and dimerization properties of the RNA polymerase I transcription factors UBF1 and UBF2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1301–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Xie W. Q., Smith S. D., Singer H. A., Rothblum L. I. Differential phosphorylation and localization of the transcription factor UBF in vivo in response to serum deprivation. In vitro dephosphorylation of UBF reduces its transactivation properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Mougey E. B., Sollner-Webb B. The Xenopus ribosomal DNA 60- and 81-base-pair repeats are position-dependent enhancers that function at the establishment of the preinitiation complex: analysis in vivo and in an enhancer-responsive in vitro system. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5093–5104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Half helical turn spacing changes convert a frog into a mouse rDNA promoter: a distant upstream domain determines the helix face of the initiation site. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):52–62. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paull T. T., Haykinson M. J., Johnson R. C. The nonspecific DNA-binding and -bending proteins HMG1 and HMG2 promote the assembly of complex nucleoprotein structures. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1521–1534. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Energetics of B-to-Z transition in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., McStay B., Schultz M. C., Bell S. P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers bind an essential polymerase I transcription factor, xUBF. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1779–1788. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Pape L. K., Henderson S. L., Ryan K., Paalman M. H., Lopata M. A., Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B. Enhancers for RNA polymerase I in mouse ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4816–4825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H. Sequence elements essential for function of the Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4282–4288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S. Ribosomal gene promoter domains can function as artificial enhancers of RNA polymerase I transcription, supporting a promoter origin for natural enhancers in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):464–468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Smith S. D., Reeder R. H., Rothblum L. rUBF, an RNA polymerase I transcription factor from rats, produces DNase I footprints identical to those produced by xUBF, its homolog from frogs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3810–3812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Chow C. S., Lippard S. J. High-mobility-group 1 protein mediates DNA bending as determined by ring closures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9465–9469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam C. D., Pikaard C. S. Cooperative binding of the Xenopus RNA polymerase I transcription factor xUBF to repetitive ribosomal gene enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4970–4980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radebaugh C. A., Matthews J. L., Geiss G. K., Liu F., Wong J. M., Bateman E., Camier S., Sentenac A., Paule M. R. TATA box-binding protein (TBP) is a constituent of the polymerase I-specific transcription initiation factor TIF-IB (SL1) bound to the rRNA promoter and shows differential sensitivity to TBP-directed reagents in polymerase I, II, and III transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):597–605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read C. M., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Driscoll P. C., Norman D. G. Solution structure of a DNA-binding domain from HMG1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3427–3436. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo R. M., Rendón M. C., Torreblanca J., García-Herdugo G., Moreno F. J. Characterization and immunolocalization of RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF with anti-NOR serum in protozoa, higher plant and vertebrate cells. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Grummt I. Transcription complex formation at the mouse rDNA promoter involves the stepwise association of four transcription factors and RNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24588–24595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp G., Santori F., Carles C., Riva M., Grummt I. The HMG box-containing nucleolar transcription factor UBF interacts with a specific subunit of RNA polymerase I. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):190–199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Langowski J., Baldwin R. L. DNA flexibility studied by covalent closure of short fragments into circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Lowe D., Yang-Yen H. F., O'Mahony D., Rose K., Chen K., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of factors that direct transcription of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3105–3116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Oriahi E., Yang-Yen H. F., Xie W. Q., Chen C., Rothblum L. I. Interaction of RNA polymerase I transcription factors with a promoter in the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1677–1685. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kato H., Ishikawa Y., Hisatake K., Tashiro K., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Sequence-specific binding of a transcription factor TFID to the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13836–13842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A., van Weperen W. W., van der Vliet P. C. POU proteins bend DNA via the POU-specific domain. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3007–3014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit R., Schnapp A., Kuhn A., Rosenbauer H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription factor mUBF is phosphorylated by casein kinase II in the C-terminal hyperacidic tail which is essential for transactivation. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2211–2218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Kraulis P. J., Hill C. S., Raine A. R., Laue E. D., Thomas J. O. Structure of the HMG box motif in the B-domain of HMG1. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., Rothblum L. I. Domains of the rat rDNA promoter must be aligned stereospecifically. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1266–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Clevers H. Sequence-specific interaction of the HMG box proteins TCF-1 and SRY occurs within the minor groove of a Watson-Crick double helix. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]