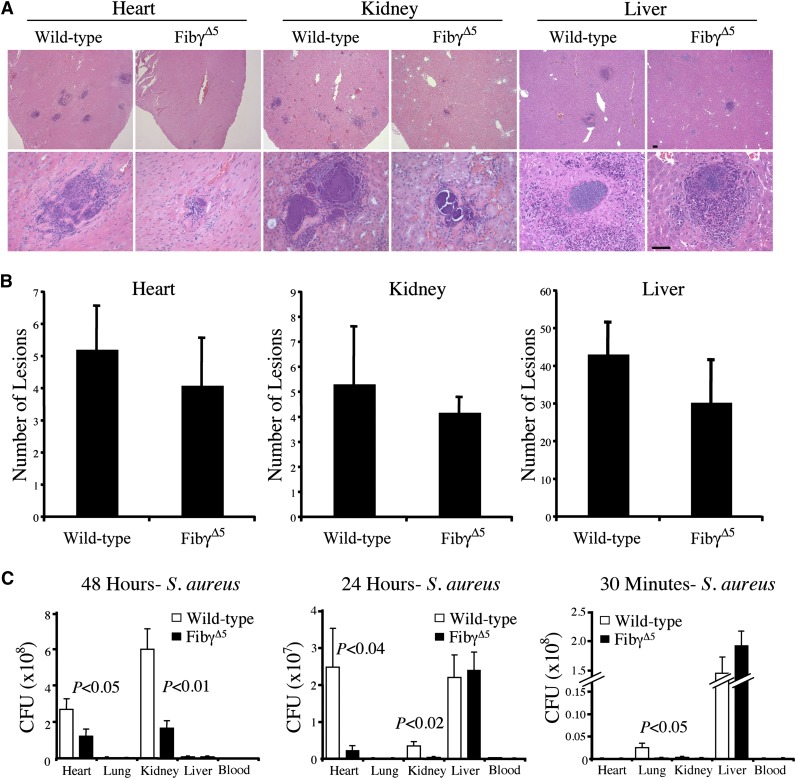
Figure 5.
Comparative analyses of abscess formation and bacterial burden in tissue from FibγΔ5 and wild-type mice following intravenous S. aureus infection. (A) Representative hematoxylin/eosin-stained sections of heart, kidney, and liver from wild-type and FibγΔ5 mice collected 48 hours after intravenous infection with 2.5 × 108 CFUs wild-type S. aureus. Images were captured using an Axioplan 2 microscope with Axiovision Image analysis software (version 4.8.1; Carl Zeiss Microimaging). Scale bar represents 100 μm (upper panels) and 50 μm (lower panels). (B) Bacterial lesion counts in tissue sections prepared from heart, kidney, and liver of wild-type and FibγΔ5 mice 48 hours after intravenous infection. Data are presented as the mean number of lesions per tissue midline section ± standard error of the mean (SEM) with N = 5 per group. (C) Bacterial burdens observed in major organs of FibγΔ5 and control mice at 48 hours (left panel), 24 hours (middle panel), and 30 minutes (right panel) following intravenous injection of 2.5 × 108 CFUs S. aureus (N = 5 per group per time point). Values in solid tissues are the total mean CFUs ± SEM within the entire organ as determined by serial plating aliquots of tissue homogenates. Values in blood are the mean CFUs ± SEM per milliliter in whole blood as determined by plating serial dilutions of whole blood collected from the inferior vena cava. The data were analyzed using the Student t test.