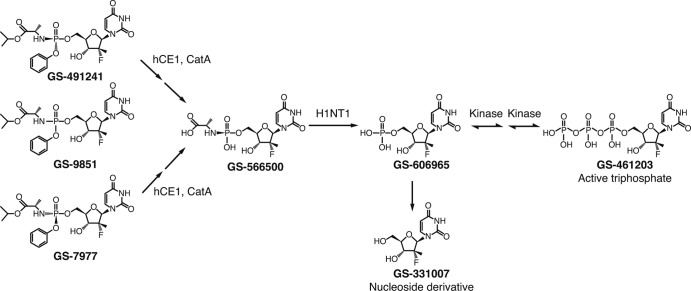
Fig 1.
Schematic of the proposed metabolic pathway of GS-9851. GS-9851 is a mixture of two diastereoisomers, GS-491241 and GS-7977. Studies in vitro demonstrated that GS-9851 is metabolized in the plasma to the intermediate GS-566500 and to the inactive nucleoside derivative GS-331007 (step not shown). Inside the hepatocyte, both GS-491241 and GS-7977 undergo hydrolysis of the carboxyl ester catalyzed by the hepatically expressed carboxyl esterase 1 (hCE1) and cathepsin A (CatA) to form GS-566500. GS-566500 is further hydrolyzed by the histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 1 (HINT1) to either GS-331007 or a uridine monophosphate, GS-606965 (step not shown). GS-606965 is further phosphorylated to the nucleotide diphosphate GS-607596 (step not shown) and then to the active triphosphate NS5B inhibitor GS-461203.