Fig 7.
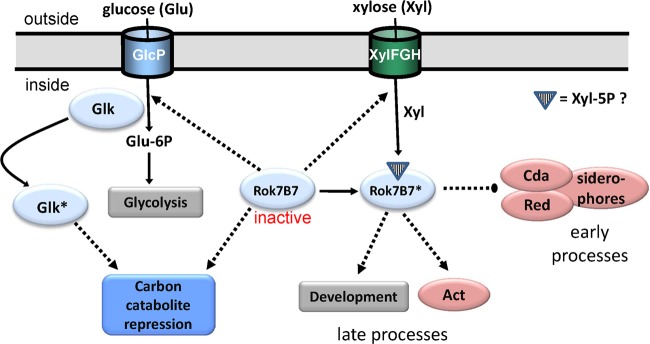
Model for the Rok7B7 regulatory network. Our data show that active Rok7B7 (indicated with an asterisk) activates actinorhodin (Act) production and development (as shown previously for its orthologue, Rep [22]), which explains the delayed development and Act production in the rok7B7 null mutant. Conversely, the production of the secondary metabolites Red, CDA, and siderophores is upregulated. Deletion of rok7B7 (presented in the model as “inactive Rok7B7”) results in enhanced expression of GlcP, Glk, and XylFGH as well as induction of CCR (including Glk-independent CCR). During glucose utilization, Glk is likely posttranslationally activated (shown as Glk*), resulting in CCR (11). Solid lines, conversion or pathway; dotted lines, regulation (arrows represent activation, large dots indicate repression). We speculate that a metabolic derivative of xylose, such as xylose-5P, acts as a ligand for Rok7B7, thus activating the protein.
