Fig 8.
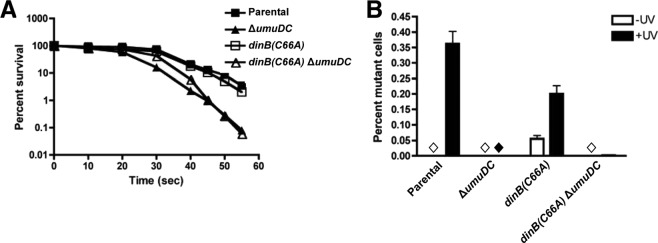
dinB(C66A) cells are not sensitive to UV irradiation but exhibit a decrease in UV-induced mutagenesis compared to isogenic dinB+. (A) Graph depicting survival of cells expressing dinB(C66A) from the chromosome compared to parental, ΔumuDC, and dinB(C66A) ΔumuDC strains. Means and 1 SD are shown. (B) Mutagenesis was measured as loss of function in a galactose mutation assay, as described in Materials and Methods. The dinB(C66A) allele is present on the chromosome and expressed from its native promoter. The bars represent means and 1 SD. The diamonds indicate no mutants were detected. The mutation frequency was assessed in three biological replicates. The total numbers of colonies examined were 7,190 (−UV) and 8038 (+UV) for the parental strain, 9,594 (−UV) and 34,770 (+UV) for the ΔumuDC strain, 9,012 (−UV) and 9,857 (+UV) for the dinB(C66A) strain, and 13,010 (−UV) and 37,729 (+UV) for the dinB(C66A) ΔumuDC strain.
